1. Respiratory substrates are the organic substances which are ________ during respiration to liberate energy.
(a) Oxidised
(b) Reduced
(c) Synthesised
(d) Both (a) and (b)
2. Complete the following biochemical equation of respiration and select the correct answer.

(a) 6CO2 + 12H2O + Energy
(b) 12CO2 + 4H2O + Energy
(c) 12CO2 + 6H2O + Energy
(d) 6CO2 + 6H2O+ Energy
3. Seeds are respire in
(a) Presence of O2
(b) Presence of CO
(c) Absence of O2
(d) Both (a) and (c).
4. Rise in the water level from X to Y in the given experimental set-up demonstrates.
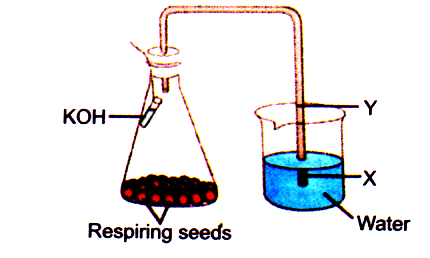
(a) Aerobic respiration
(b) Anaerobic respiratio
(c) Photosynthesis
(d) Transpiration pull.
5. The pathway of respiration common in all living organisms is X; it occurs in the Y and the products formed are two molecules of Z.
Identity X, Y and Z in the above paragraph and select the correct answer.
| X | Y | Z | |
| (a) | EMP pathway | Mitochondrion | Pyruvic acid |
| (b) | EMP pathway | Cytoplasm | Pyruvic acid |
| (c) | Krebs’ cycle | Cytoplasm | Acetyl CoA |
| (d) | Krebs’ cycle | Mitochondrion | Acetyl CoA |
6. Select the wrong statement with respect to glycolysis.
(a) It occurs outside mitochondria
(b) It is an anaerobic phase
(c) Glucose undergoes partial oxidation to form 2 molecules of pyruvic acid
(d) Glucose is phosphorylated to glucose-6-phosphate by isomerase enzyme.
7. The flow chart given below shows the steps in glycolysis. Select the option that correctly fills in the missing steps A, B, C and D.
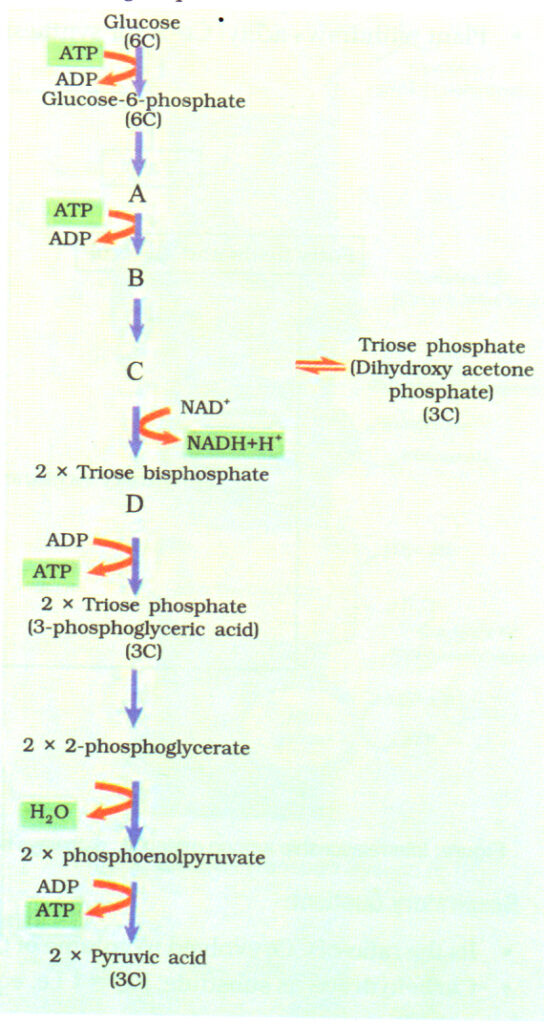
| A | B | C | D | |
| (a) | Fructose-6- phosphate | Fructose-1 6-bisphosphate | 3-PGAL | 1,3-bisphosphoglyceric acid |
| (b) | Fructose-1 6-bisphosphate | 3-PGAL | 1,3-bisphospho- glyceric acid | 3-PGA |
| (c) | 3-PGA | 1, 3-bisphospho- glyceric acid | 3-PGAL | Fructose-1 6- bisphosphate |
| (d) | Fructose-1 6-bisphosphate | Fructose-6 -phosphate | 3-PGAL | 1,3-bisphospho-glyceric acid |
8. What is true about the end products of glycolysis?
(a) 2 pyruvic acid + 2 ATP + 2NADH2
(b) 2 pyruvic acid + 2NADH
(c) 1 pyruvic acid + 2 ATP + 2NADH2
(d) 2 pyruvic acid + 1 ATP + 1NADH2
9. During the process of aerobic respiration, (i) gets oxidised and its electrons get transferred to the electron transport chain while in photosynthesis, (ii) gets oxidised to transfer molecules to the electron transport chain.
(a) (i)-glucose, (ii)-xanthophyll
(b) (i)-carbon dioxide, (ii)-xanthophyl
(c) (i)-carbon dioxide, (ii)-chlorophyll-a
(d) (i)-glucose, (ii)-chlorophyll-a
10. Which of the following options does not hold good regarding anaerobic respiration or fermentation?
(a) Occurs inside the mitochondria
(b) Partial breakdown of glucose occur
(c) Net gain of only 2 ATP molecules
(d) None of these
11. Identify the enzymes 1 and 2 in the given reaction and select the correct option.

| 1 | 2 | |
| a | Alcohol dehydrogenase | Pyruvate decarboxylase |
| b | Alcohol decarboxylase | Pyruvate dehydrogenase |
| c | Pyruvate decarboxylase | Alcohol dehydrogenase |
| d | Pyruvate dehydrogenase | Alcohol dehydrogenase |
12. What does A, B and C depict in the given pathways of anaerobic respiration?

| A | B | C | |
| a | NADH + H+ →NAD+ | NAD+ → NADH + H+ | NAD+ → NADH + H+ |
| b | NADH + H+ → NAD+ | NADH + H+ → NAD+ | NAD+ → NADH + H+ |
| c | NAD+ → NADH + H+ | NADH + H+ → NAD+ | NADH + H+ → NAD+ |
| d | NAD+ → NADH + H+ | NADH + H+ → NAD+ | NAD+ → NADH + H+ |
13. Though vertebrates are aerobes, but their (i) show anaerobic respiration during (ii). During this, (iii) of skeletal muscle fibres is broken down to release lactic acid and energy. Lactic acid, if accumulates causes muscle fatigue.
Fill up the blanks in the above paragraph and select the correct option.
| (i) | (ii) | (iii) | |
| a | skeletal muscles | heavy exercise | glucose |
| b | skeletal muscles | mild exercise | glycogen |
| c | skeletal muscles | heavy exercise | glycogen |
| d | cardiac muscles | heavy exercise | glycogen |
14. Select the incorrectly matched pair.
(a) End products of alcoholic – Ethanol + CO2 fermentation
(b) End products of lactic – Lactic acid + CO2 acid fermentation
(c) Glycolysis – Cytoplasm
(d) Key product of glycolysis – Pyruvic acid
15. Site of Krebs’ cycle in mitochondria is
(a) Outer membrane
(b) Matrix
(c) Oxysomes
(d) Inner membrane.
16. Fate of pyruvic acid during aerobic respiration is
(a) Lactic acid fermentation
(b) Alcoholic fermentation
(c) Oxidative decarboxylation
(d) Oxidative phosphorylation.
17. Identify A and B in the given reaction.

| A | B | |
| (a) | PEP | CO2 |
| (b) | Acetyl CoA | CO2 |
| (c) | CO2 | H2O |
| (d) | Acetyl CoA | H2O |
18. Which step is called gateway step /link reaction in aerobic respiration?
(a) Glycolysis
(b) Formation of acetyl coenzyme A
(c) Citric acid formation
(d) ETS terminal oxidation
19. Alternate name of Krebs’ cycle is
(a) TCA cycle
(b) Citric acid cycle
(c) both (a) and (b)
(d) none of these.
20. Krebs’ cycle starts with the formation of a six carbon compound by reaction between
(a) Fumaric acid and pyruvic acid
(b) OAA and acetyl Co
(c) Malic acid and acetyl CoA
(d) Succinic acid and pyruvic acid.
21. Which of the following is a 4-carbon compound?
(a) Oxaloacetic acid
(b) Phosphoglyceric acid
(c) Ribulose bisphosphate
(d) Phosphoenol pyruvate
22. Identify X, Y and Z in the given diagram representing steps of citric acid cycle and select the correct option.
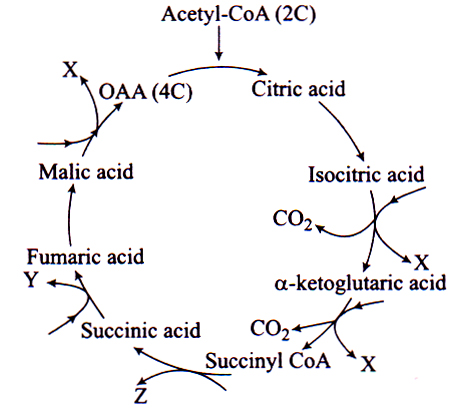
| X | Y | Z | |
| (a) | GTP | NADH2 | FADH2 |
| (b) | FADH2 | NADH2 | GTP |
| (c) | NADH2 | FADH2 | GTP |
| (d) | CO2 | NADH2 | ADP |
23. Krebs’ cycle is also called metabolic sink as it is a common pathway for
(a) Carbohydrates, fats and proteins (amino acids
(b) Carbohydrates and fats only
(c) Carbohydrates and organic acids only
(d) Proteins and fats only.
24. The intermediate product between a-ketoglutaric acid and succinic acid in TCA cycle is
(a) Acetyl CoA
(b) Succinyl CoA
(c) Fumarate
(d) Oxalosuccinic acid.
25. Select the correct sequence of formation of given intermediates of Krebs’ cycle.
(a) Succinate → Malate → Fumarate → OAA
(b) Fumarate → Succinate → Malate → OAA
(c) Succinate → Fumarate → Malate → OAA
(d) Malate → Fumarate → Succinate →OAA
26. Substrate level phosphorylation occurs during which step of Krebs’ cycle?
(a) Succinyl CoA → Succinic acid
(b) Isocitric acid → Oxalosuccinic acid
(c) Oxalosuccinic acid → α-ketoglutaric acid
(d) Malic acid → OAA
27. The first 5C dicarboxylic acid in Krebs’ cycle which is used in nitrogen metabolism is
(a) OAA
(b) Citric acid
(c) α-ketoglutaric acid
(d) Acetyl coenzyme A.
28. Categories the given equation under respective phases and select the correct option.
(i) C6H12O6 + 2NAD+ + 2ADP + 2Pi→2C3H4O3 + 2ATP + 2NADH + 2H+
(ii) Pyruvic acid + 4NAD+ + FAD+ + 2H2O + ADP + Pi → 3CO2 + 4NADH + 4H+ + ATP + FADH2
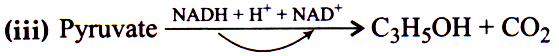
| I | II | III | |
| a | Glycolysis | Fermentation | Krebs’ cycle |
| b | Krebs’ cycle | Fermentation | Glycolysis |
| c | Krebs’ cycle | Glycolysis | Fermentation |
| d | Glycolysis | Kreb’s cycle | Fermentation |
29. Which of the following steps of respiration is amphibolic?
(a) Glycolysis
(b) Oxidative decarboxylation of pyruvate
(c) TCA cycle
(d) Oxidative phosphorylation
30. When two molecules of acetyl CoA enter the TCA cycle, net again at the end of the cycle is
(a) 2NADH2 + 2FADH2 + 1GTP
(b) 3NADH2 + 2FADH2 + 2GTP
(c) 6NADH2 + 2FADH2 + 2GTP
(d) 3NADH2 + 1FADH2 + 4GTP
31. All of the following processes can release CO2 except
(a) Alcoholic fermentation
(b) Oxidative decarboxylation and Krebs’ cycle
(c) Oxidative phosphorylation
(d) Conversion of α-ketoglutaric acid to succinic acid.
32. Select the option that correctly fills the blanks in the following statement.
A. Glucose has (i) carbon atoms, pyruvic acid has (ii) carbon atoms and the acetyl group has (iii) carbon atoms.
B. Electrons enter the electron transport system as parts of hydrogen atoms attached to (i) and (ii).
| A | B | |
| (a) | (i)-6, (ii)-4, (iii)-3 | (i)-NADH, (ii)-FADH2 |
| (b) | (i)-6, (ii)-3, (iii)-2 | (i)-NADH, (ii)-FADH2 |
| (c) | (i)-6, (ii)-3, (iii)-2 | (i)-ATP, (ii)-GTP |
| (d) | (i)-6, (ii)-4, (iii)-3 | (i)-ATP, (ii)-GTP |
33. Identify P, Q, R and S in the given diagram of electron transport system.
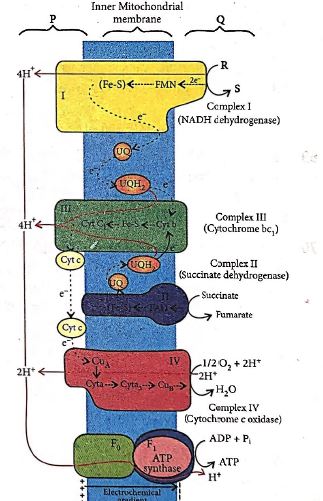
| P | Q | R | S | |
| a | Matrix | Outer chamber | FMNH2 | NADH2 |
| b | Inter-membrane space | Matrix | NADH+H+ | NAD+ |
| c | Inter-membrane space | Cristae | NAD+ | NADH + H+ |
| d | Cristae | Outer chamber | NADH+H+ | NAD+ |
34. Match column I with column II and select the correct option from the given codes.
| Column I | Column II | ||
| A. | Glycolysis | i | Inner mitochondrial membrane |
| B. | TCA cycle | ii | Mitochondrial matrix |
| C. | ETS | iii | Cytoplasm |
(a) A- (iii), B- (i), C- (ii)
(b) A- (iii), B- (ii), C- (i)
(c) A- (i), B- (ii), C- (iii)
(d) A- (ii), B- (i), C- (iii)
35. In the electron transport system present in the inner mitochondrial membrane complexes I and IV are respectively
(a) NADH dehydrogenase and FADH2
(b) FADH2 and NADH dehydrogenase
(c) NADH dehydrogenase and cytochrome c oxidase complex
(d) NADH dehydrogenase and ATP synthase.
36. Oxidation of one NADH and one FADH2 respectively gives rise to ______ and _____ ATP molecules.
(a) 3,2
(b) 2,1
(c) 2,3
(d) 1,1
37. Study the incorrect statement with respect to an overview of the electron transport system (ETS).
(a) Ubiquinone receives reducing equivalents via., FADH2 (complex II) that is generated during oxidation of succinate in the TCA cycle.
(b) As the electrons move down the system, energy is released and used to form ATP.
(c) 2ATPs are formed for every pair of electrons that enters by way of NADH and 3ATPs are formed for every pair of electrons that enters by way of FADH2.
(d) Oxygen, the final e– acceptor becomes a part of water.
38. Read the given statements and select the correct option.
Statement 1: During photophosphorylation of photosynthesis), light energy is utilised for the production of proton gradient during ATP synthesis.
Statement 2: In respiration, energy of oxidation- reduction is utilised for the phosphorylation and thus the process is called oxidative phosphorylation.
(a) Both statement 1 and 2 are correct.
(b) Statement 1 is correct but statement 2 is incorrect
(c) Statement 1 is incorrect but statement 2 is correct
(d) Both statements 1 and 2 are incorrect.
39. Identify A and B in the given diagram showing ATP synthesis in mitochondria.
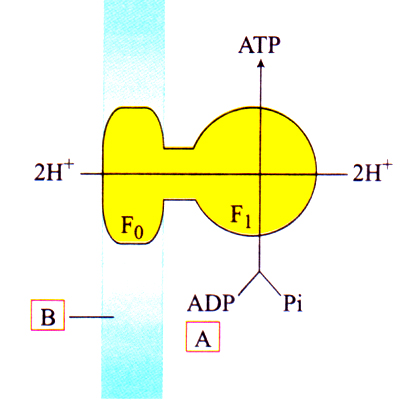
(a) A = Mitochondrial matrix
B = Outer mitochondrial membrane
(b) A = Mitochondrial matrix
B = Inner mitochondrial membrane
(c) A = Cell cytoplasm
B = Inner mitochondrial membrane
(d) A = Cell cytoplasm
B = Outer mitochondrial membrane
40. As per chemiosmotic coupling hypothesis in mitochondria, protons accumulate in the
(a) Outer membrane
(b) Inner membrane
(c) Intermembrane space
(d) Matrix
41. Study the following statements regarding chemiosmotic hypothesis in mitochondria and select the correct ones.
(i) F1 headpiece contains the site for the synthesis of ATP from ADP + Pi.
(ii) F0 part forms the channel through which protons cross the inner membrane
(iii) For each ATP produced, 2H+ pass through F0 from the intermembrane space to the matrix down the electrochemical proton gradient.
(a) (i) and (ii)
(b) (ii) and (iii)
(c) (i) and (iii)
(d) (i), (ii) and (iii)
42. Which of the following cellular metabolic processes can occur both in the presence or absence of O2?
(a) Glycolysis
(b) Fermentation
(c) TCA cycle
(d) Electron transport coupled with chemiosmosis
43. The balance sheet for ATP production in glycolysis has been given below. Select the option which correctly fills up the blanks for P, Q, R and S. [‘X’ stands for ‘nil’].
| Steps | ATP Utilisation | ATP Production | |
| 1. | Glucose → Glucose-6-phosphate | P | X |
| 2. | Fructose-6-phosphate→ fructose-1, 6-bisphosphate | 1 | Q |
| 3. | 1, 3-bisphospho-glyceric acid → 3-phospho-glyceric acid | X | R |
| 4. | 2-Phosphoenol pyruvic acid → Pyruvic acid | S | 2 |
| P | Q | R | S | |
| (a) | 1 | X | X | 2 |
| (b) | 1 | X | 2 | X |
| (c) | 2 | 1 | X | 1 |
| (d) | X | 1 | 2 | X |
44. Refer to the given figure and select the correct option for A, B, C and D.
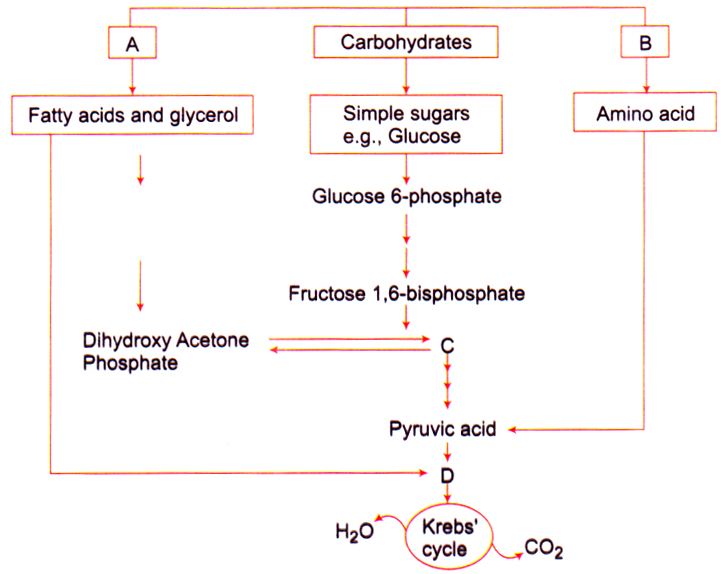
| A | B | C | D | |
| a | Fats | Proteins | 3-PGAL | Acetyl CoA |
| b | Fats | Proteins | 3-PGAL | CO2 |
| c | Proteins | Fats | Acetyl CoA | PEP |
| d | Proteins | Fats | PEP | Acetyl CoA |
45. Respiratory pathway is
(a) Catabolic
(b) Amphibolic
(c) Anabolic
(d) Endergonic
46. Which out of the following statements is incorrect?
(a) The breakdown product of glucose which enters into mitochondrion during aerobic respiration is pyruvic acid generated in the cytosol.
(b) When the electrons pass from one carrier to another via complex I to IV in the electron transport chain, they are coupled to ATP synthase (complex V) for the production of ATP from ADP and Pi.
(c) The ratio of volume of O2 consumed in respiration to the volume of CO2 evolved is called as the respiratory quotient (RQ).
(d) Compensation point is the point reached in a plant when the rate of photosynthesis is equal to the rate of respiration.
47. Refer the given equation.
2(C51H98O6) + 145O2 → 102CO2 + 98H2O + Energy
The RQ in this case is
(a) 1
(b) 0.7
(c) 1.45
(d) 1.62
48. Consider the following statements with respect to respiration.
(i) Glycolysis occurs in the cytoplasm of the cell.
(ii) Aerobic respiration takes place within the mitochondria.
(iii) Electron transport system is present in the outer mitochondrial membrane.
(iv) C51H98O6 is the chemical formula of tripalmitin, a fatty acid.
(a) (i), (ii) and (iv) are correct
(b) (ii), (iii) and (iv) are correct
(c) (iii), (iv) and (v) are correct
(d) (ii), (iv) and (v) are correct.
49. RQ of proteins, carbohydrates, fats and organic acids are in order
(a) < 1, 1, < 1, > 1
(b) > 1, < 1, 1, 1
(c) 1, 1, 0, -1
(d) 0, < 1, 1, > 1
50. RQ in anaerobic respiration is
(a) 0.7
(b) 0.9
(c) Unity
(d) Infinity.
51. Which of these statements is incorrect?
(a) Enzymes of TCA cycle are present in mitochondrial matrix
(b) Glycolysis occurs in cytosol
(c) Oxidative phosphorylation takes place in outer mitochondrial membrane
(d) Glycolysis operates as long as it is supplied with NAD that can pick up hydrogen atoms
52. What is the role of NAD+ in cellular respiration?
(a) It function as an enzyme.
(b) It functions as an electron carrier.
(c) It is the final electron acceptor for anaerobic respiration.
(d) It is a nucleotide source for ATP synthesis.
53. Which statement is wrong for Krebs’ cycle?
(a) There are three points in the cycle where NAD+ is reduced to NADH + H+
(b) There is one point in the cycle where FAD+ is reduced to FADH2
(c) During conversion of succinyl CoA to succinic acid, a molecule of GTP is synthesised
(d) The cycle starts with condensation of acetyl group (acetyl CoA) with pyruvic acid to yield citric acid
54. Cytochromes are found in
(a) Lysosomes
(b) Matrix of mitochondria
(c) Outer wall of mitochondria
(d) Cristae of mitochondria
55. Which of the metabolites is common to respiration mediated breakdown of fats, carbohydrates and proteins?
(a) Fructose 1, 6-bisphosphate
(b) Pyruvic acid
(c) Acetyl CoA
(d) Glucose-6-phosphate
| Question No. | Answer |
| 1. | a |
| 2. | d |
| 3. | d |
| 4. | a |
| 5. | b |
| 6. | d |
| 7. | a |
| 8. | a |
| 9. | d |
| 10. | a |
| 11. | c |
| 12. | c |
| 13. | a |
| 14. | b |
| 15. | b |
| 16. | c |
| 17. | b |
| 18. | b |
| 19. | c |
| 20. | b |
| 21 | a |
| 22. | c |
| 23. | a |
| 24. | b |
| 25. | c |
| 26. | a |
| 27. | c |
| 28. | d |
| 29. | c |
| 30. | c |
| 31. | c |
| 32. | b |
| 33. | b |
| 34. | b |
| 35. | c |
| 36. | a |
| 37. | c |
| 38. | a |
| 39. | b |
| 40. | c |
| 41. | d |
| 42. | a |
| 43. | b |
| 44. | a |
| 45. | b |
| 46. | c |
| 47. | b |
| 48. | a |
| 49. | a |
| 50. | d |
| 51. | c |
| 52. | b |
| 53. | d |
| 54. | d |
| 55. | c |
6 thoughts on “”