MCQ on Cell Cycle and Cell Division MCQ on Cell Cycle and Cell Division
1. Dictyotene a is prolonged
a) Leptotene
b) Pachytene
c) Diplotene
d) Zygotene
2. Which of the following is unique to mitosis and not a part of meiosis?
a) Homologous chromosomes behave independently
b) Chromatids are separated during anaphase
c) Homologous chromosomes pair and form bivalents
d) Homologous chromosomes crossover
3. Spindle fibre is made up of
a) Humulin
b) Intermediate filament
c) Flagellin
d) Tubulin
4. There are three genes a,b,c with percentage of crossing over between a and b is 20%, b and c is 28% and a and c is 8%. What is the sequence of genes on chromosome?
a) b,a,c
b) a,b,c
c) a,c,b
d) None of these
5. See the diagrams carefully and identify the different stages of mitosis (A-C) by choosing appropriate options given below
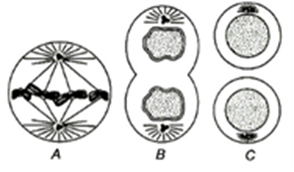
a) A-Metaphase; B-Telophase; C-Interphase
b) A-Telophase; B-Metaphase; C-Prophase
c) A-Anaphase; B-Telophase; C-Interphase
d) A-Telophase; B-Anaphase; C-Prophase
6. During which stage of meiosis, do tetrads line up at the equator?
a) Prophase-I
b) Telophase-I
c) Metaphase-I
d) Anaphase-I
7. The anaphase promoting complex is activated by
a) M cdk cyclin
b) G1 cdk cyclin
c) S cdk cyclin
d) Transaction factor
8. A cell plate is laid down during
a) Cytokinesis
b) Karyokinesis
c) Interphase
d) None of these
9. During which stage of meiosis, do the sister chromatids begin to move towards the poles?
a) Prophase-I
b) Telophase-I
c) Anaphase-II
d) Anaphase-I
MCQ on Cell Cycle & Cell Division
We would Like your Valuable Feedback
10. In a cell cycle, which structures serves as the site of attachment of spindle fibers?
a) Chromosomes
b) Histone
c) Chromonemeta
d) Kinetochore
11. Identify the diagram and name the phase of meiosis carefully
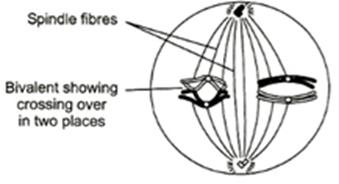
a) Telophase-I
b) Anaphase-I
c) Metaphase-I
d) Prophase-I
12. Which of the following serves as mitotic spindle poison?
a) Ca(2+)
b) Mg(2+)
c) Tubulin
d) Colchicine
13. Chromosomes are visible with chromatids at which phase of mitosis?
a) Interphase
b) Prophase
c) Metaphase
d) Anaphase
14. RNA and proteins are formed in
a) G1-phase
b) G2-phase
c) S-phase
d) G0-phase
15. Give the name of the phases of meiosis, in which
I. the chromosome number is reduced to haploid state
II. the amount of DNA is reduced to haploid state
The correct option is
a) Anaphase-II; anaphase-I
b) Anaphase-I, metaphase-II
c) Anaphase-I, anaphase-II
d) Anaphase-II, metaphase-I
16. What type of cell division takes place in the functional megaspore initially in angiosperms?
a) Homeotypic without cytokinesis
b) Reductional without cytokinesis
c) Somatic followed by cytokinesis
d) Meiotic followed by cytokinesis
17. Which of the following statements are correct for multicellular cell division?
I. Cell division brings about embryonic development and growth
II. It plays a role in repair and maintenance of the body
III. It is important for reproduction
The correct option is
a) Only I
b) I and III
c) Only II
d) I, II and III
18. Meiosis involves two sequential cycles of …A… called meiosis-I and meiosis-II but only a single cycle of …B…
Identify A and B to complete the given statement
a) A-nuclear and cell division, B-DNA replication
b) A-cell division, B-DNA replication
c) A-DNA replication, B-cell division
d) A-nuclear division, B-DNA replication
19. During, meiosis-I, the bivalent chromosomes clearly appear as tetrads during
a) Diakinesis
b) Diplotene
c) Leptotene
d) Pachytene
20. DNA replicates
a) Twice in each cell cycle
b) Only once in each cell cycle
c) Once in mitotic cell cycle, once in meiotic-I (reductional division) and once in meiotic-II (equational division)
d) None of the above
1 (c)
In oocytes, a special, extremely prolonged form of diplotene occurs, called dictyotene. The primary oocyte undergoes the first three substages of prophase-I (laptotene, zygotene and pachytene) during late foetal life.
The process is then, suspended during diplotene until puberty or thereafter. Therefore, dictyotene, lasts for months or even years. Diplotene is also known as diplonema
2 (a)
During mitosis, all the chromosomes behave independently while during meiosis, homologous chromosomes pair up through synapsis and form bivalents in zygotene substage of prophase-I, then in pachytene substage, crossing over occurs between homologous chromosomes and during diplotene substage of prophase-I of meiosis chiasma formation takes place.
During anaphase of both mitosis and meiosis, chromatids are separated and pulled towards opposite poles.
3 (d)
Microtubules are hollow, cylindrical structure built from tubulin protein. The mitotic spindle involved in separation of replicated chromosomes during mitosis is assembly of microtubules.
5 (a)
A. Metaphase Spindle fibers attaches to kinetochores of chromosomes
Chromosomes are moved to spindle equator and get aligned along metaphase plate through spindle fibers of both poles
B. Telophase Chromosomes cluster at opposite spindle poles and their identify is lost as discrete elements
Nuclear envelope assembles around the chromosome clusters
Nucleolus, Golgi complex and ER reform
C. Interphase It is the duration which is a variable depending on the function of cell.
Just before nuclear division, the DNA of chromosome replicates thus, it becomes doubled.
During this phase, chromosome material is in the form of very loosely coiled threads called chromatin
6 (c)
During metaphase-I of meiosis, tetrads line up at the equator.
7 (a)
M cdk cyclin activates anaphase promoting complex.
8 (a)
During cytokinesis in plant cells spindle fibers do not degenerate and forms phragmoplast and cell plate.
9 (d)
During anaphase-I of meiosis, the sister chromatids begin to move towards the poles.
10 (d)
Small disc-shaped structure at the surface of the centromeres are called kinetochores. These structures serve as the sites of attachment of spindle fibers (formed by the spindle fibers) to the chromosomes that are moved into position at the center of the cell
Hence, the metaphase is characterized by all the chromosomes coming to lie at the equator with one chromatid of each chromosome connected by its connected by its kinetochore to spindle fibers from one pole and its sister chromatid connected by its kinetochore to spindle fibers from the opposite pole
11 (c)
Meiosis-I
(i) The bivalents become arranged around the equator of the spindle, attached by their centromeres
(ii) Each pair of the homologous chromosomes is called bivalent which pair up in the process of synapsis
12 (d)
Colchicine serves as mitotic spindle poison.
13 (c)
Chromosomes are visible with chromatids at metaphase stage of mitosis. It is the best stage to observe the shape, size and number of chromosomes.
14 (b)
The main events which take place in G1-phase are:
Intensive cellular synthesis,
Pooling of nucleotides for synthesis of rRNA.
Synthesis of enzymes and ATP storage,
Synthesis of NHC protein, carbohydrates, liquids, etc.
15 (c)
Anaphase-I, anaphase-II.
In anaphase-I chromosome become half in number. Chromosomes split and move to opposite ends of the cell, both in anaphase-I and anaphase-II. The difference is that in anaphase-I, homologous pairs of chromosomes are split and in anaphase-II, sister chromatids are split
16 (a)
Initially, homeotypic cell division takes place in the functional megaspore without cytokinesis.
17 (d)
In multicellular organisms, cell division brings about embryonic development and growth and also plays an important role in repair and maintenance of the body and also in reproduction, both asexual and sexual
18 (a)
Meiosis involves two sequential cycles of nuclear and cell division called meiosis-I and meiosis-II but only a single cycle of DNA replication
19 (d)
During pachytene of meiosis-I, the chromosomes become bivalent (tetrad) in the beginning, i.e, each chromosome with two chromatids.
20 (b)
DNA replicates only once in each cell cycle (S-phase)
3 thoughts on “MCQ on Cell Cycle and Cell Division ”