MCQ on Cell Cycle and Cell Division MCQ on Cell Cycle and Cell Division
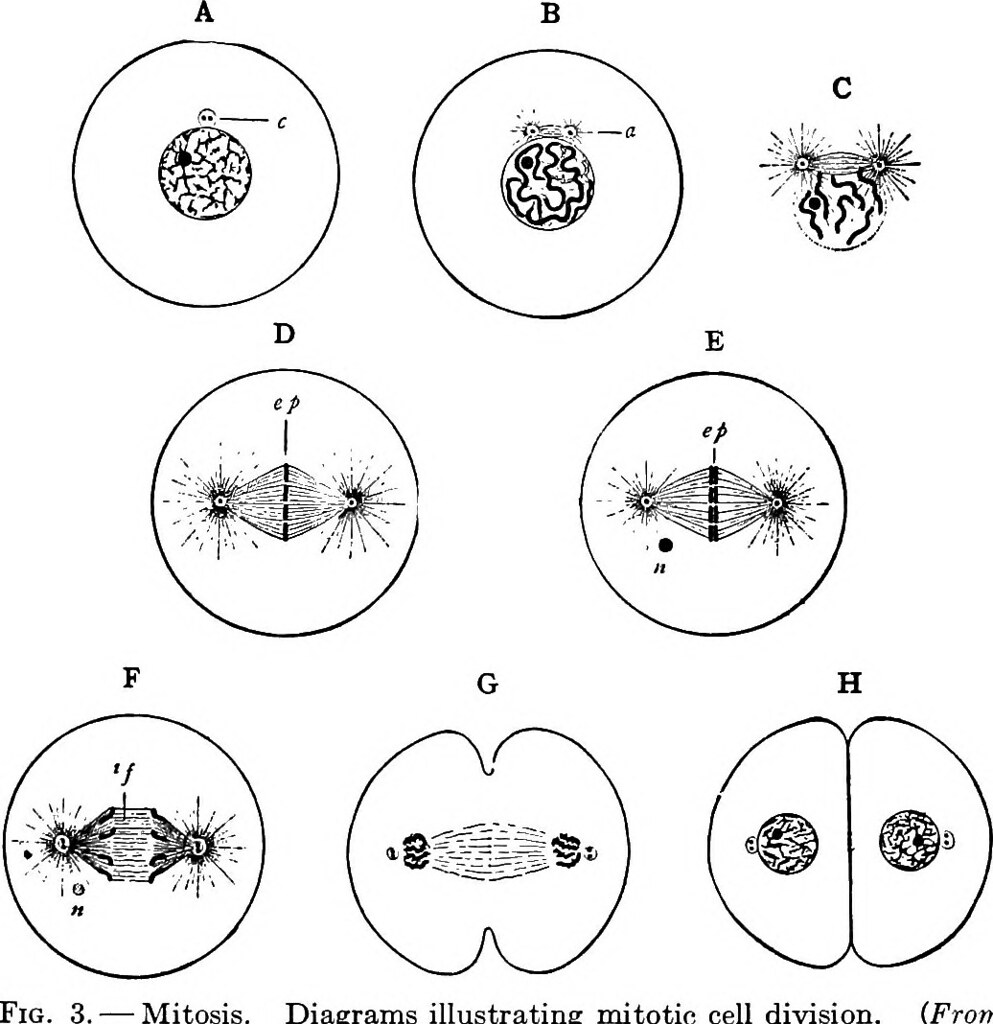
1. Select the correct sequence of a cell cycle
a) G2→M→G1→S
b) S→G2→M→G1
c) G1→S→G2→M
d) M→G1→G2→M
2. Which of the following statements are correct for meiosis?
I. Meiosis is a double division. It gives rise to four cells
II. The cells undergoing meiosis may be haploid or diploid
III. No bouquet stage is recorded
IV. Pairing or synapsis of homologous chromosomes takes place during zygotene of prophase-I and continues upto metaphase-I
Option containing correct statement is
a) I only
b) I and IV
c) II and III
d) All of these
3. Mature nerve cells are incapable of cell division. These cells are probably considered in
a) G2-phase
b) S-phase
c) Mitosis
d) G0-phase
4. Mitosis or the equational division is usually restricted to …A… cells. However, in some lower plants and in some social insects …B… cells also divide by mitosis.
Choose the correct option for A and B from the given options
A B
a) Haploid; diploid
b) Haploid; haploid
c) Diploid; diploid
d) Diploid; haploid
5.The spindles are formed of
a) Chromosome
b) Actin
c) Microtubules
d) Myosin
6. During mitosis, ER and nucleolus begin to disappear at
a) Late prophase
b) Early metaphase
c) Late metaphase
d) Early prophase
7. The plane of alignment of chromosome at the metaphase stage of cell cycle is referred to as the
a) Prophase plate
b) Metaphase plate
c) Anaphase plate
d) Telophase plate
8. From the following, identify the two correct statements with reference to meiosis
I. Bead-like structures are absent on chromosomes
II. Displacement of chiasmata occurs in diakinesis
III. Separation of two basic sets of chromosomes
IV. No division of centromere
The correct option is
a) II and III
b) II and IV
c) III and IV
d) I and III
9. Consider the following statements about colchicine
I. It is an alkaloid widely used in plant breeding for doubling the chromosome number
II. Colchicine induced polyploidy has been used in raising several varieties of horticulture and agricultural plants
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
a) Only I
b) Only II
c) Both I and II
d) None of these
10. Separation of linked genes is called
a) Linkage
b) Segregation
c) Crossing over
d) Genetic mutation
11. Sequence of four phases of cell cycle is
a) G1 →S →G2→M
b) G1 →G2 →S→M
c) S→G1 →G2→M
d)M→G1 →G2→S
12. The division of the cytoplasm is termed as
a) Karyokinesis
b) Mitosis
c) Cytokinesis
d) Meiosis
13. Cell would normally proceed to mitosis without interruption
a) Once it had started the S-period
b) Once it had entered the G2-phase
c) At anytime during cell division
d) None of the above
14. The two chromatids of a metaphase chromosome represent
a) Replicated chromosomes to be separated at anaphase
b) Homologous chromosomes of a diploid set
c) Non-homologous chromosomes joined at the centromere
d) Maternal and paternal chromosomes joined at the centromere
15. In the process of mitotic division during interphase, chromosome material remains in the form of very loosely coiled threads called
a) Chromosome
b) Chromatin
c) Chromatid
d) Microtubules
16. Which is synthesized in G1-phase?
a) DNA polymerase
b) Histones
c) Nucleolar DNA
d) Tubulin protein
17. Which of the following occurs more than one and less than five in a chromosome?
a) Chromatid
b) Chromomere
c) Centromere
d) Telomere
18. Longest phase of meiosis, is
a) Prophase-I
b) Prophase-II
c) Anaphase-I
d) Metaphase-II
19. Mitotic stages are not observed in
a) Cosmarium
b) E.coli
c) Saccharomyces
d) Chlorella
20. Crossing over is also an enzyme mediated process and the enzyme involved is called
a) Ligase
b) Polymerase
c) Recombinase
d) Endonuclease
1 (c)
The cell cycle is divided into two basic phases
(i) Interphase
(ii) M-phase (mitosis phase)
The interphase is further divided into three phases
(i) G1-phase (gap 1)
(ii) S-phase (synthesis)
(iii) G2-phase (gap 2)
The correct sequence of a cell cycle is
G1→S→G2→M
2 (b)
It is mitosis, in which both diploid and haploid cells undergoes this process.
If a diploid cell undergoes mitosis, it results in two identical diploid cells. 2n→n
If a haploid cell undergoes mitosis, the result is two identical haploid cells (n→n).
In meiosis however, a diploid cell participates that divides twice to produce four haploid cells
3 (d)
Some cells in the adult animals do not appear to exhibit division (e.g., heart cells, and many other cells divide only occasionally e.g., when there is need to replace cells that have been lost due to injury or cell death. These cells that do not divide further and exit G1-phase to enter an inactive stage called quiescent stage (G0) of the cell cycle. Cells in this stage remains metabolically active but no longer proliferate
4 (d)
A-diploid; B-haploid
5 (c)
The spindle are formed of microtubules
6 (d)
In mitosis, prophase is the longest phase of karyokinesis. In early prophase, nuclear membrane and nucleolus start disintegrating. Cell cytoskeleton, Golgi complex, ER, etc, also disappear.
7 (b)
The plane of alignment of the chromosomes at metaphase is referred to as the metaphase plat. They key features of metaphase are
(i) Spindle fibres attach to kinetochores of chromosomes
(ii) Chromosomes are moved to spindle equator and get aligned along metaphase plate through spindle fibres to both poles
8 (a)
In meiosis-I, displacement of chiasmata takes place in diakinesis and homologous chromosomes segregates during anaphase-I
9 (c)
Colchicine is an alkaloid widely used in plant breeding for doubling the chromosome number. Colchicine is extracted from the corms of Autumn crocus (Colchicum autumnale). The alkaloid does not allow the formation of spindle. Colchicine induced polyploidy has been used in raising several varieties of horticultural and agricultural plants, e.g., potato
10 (c)
Crossing over leads to separation of linked genes and recombination with the genes present on homologous chromosome to form new combinations.
11 (a)
The correct sequence of cell cycle phases is
G1 →S →G2→M.
12 (c)
There are two main ways of cell division i.e., mitosis and meiosis. In each case, division of the nucleus, called karyokinesis, occurs before the division of the cytoplasm, termed as cytokinesis
13 (a)
Cell would normally proceed to mitosis without interruption once it had started the S-period.
14 (a)
The two chromatids of a metaphase chromosome represent replicated chromosomes to be separated at anaphase.
15 (b)
During interphase, the chromosome material (DNA of chromosome) replicates and becomes doubled. Chromosome material in the form of very loosely coiled threads is called chromatin
16 (a)
G1-phase is the longest phase of the cell cycle and is also called as presynthetic or post mitotic phase. During it, the synthesis of biochemicals like RNAs, proteins, enzymes (DNA polymerase) for DNA synthesis, amino acids for histone formation, nucleotides and ATP, takes place.
17 (d)
Telomeres are the ends of chromosomes. These are required for the individuality of chromosomes. Generally, these are present more than one and less than five in a chromosome.
18 (a)
Meiosis is division necessary for the formation of gamates in animals and spores in plants. Prophase-I is longest phase of meiosis and composed of leptotene, zygotene, pachytene, diplotene and diakinesis.
20 (c)
Crossing over is also an enzyme mediated process and the enzyme involved is called recombinase
1 thought on “MCQ on Cell Cycle and Cell Division”