1.The correct sequence of phases in cell cycle is: (Page 163, XI NCERT)
(1) G1→S→G2→MG1→S→G2→M
(2) M→G1→G2→SM→G1→G2→S
(3) G1→G2→S→MG1→G2→S→M
(4) S→G1→G2→MS→G1→G2→M
2. During cell growth, DNA synthesis takes place in (PAGE 163, XI NCERT)
(1) S-phase
(2) G1-phase
(3) G2-phase
(4) M-phase
3. Consider the given two statements: (Page 163, XI NCERT)
l. During G1 phase the cell is metabolically active and continuously grows but does not replicate its DNA.
ll. During G2 phase, proteins are synthesized in preparation for mitosis while cell growth continues.
Of the two statements:
(1) Only l is correct
(2) Only ll is correct
(3) Both l and ll are correct
(4) Both l and ll are incorrect
4. Which is the longest phase of the cell cycle? (PAGE 163, XI NCERT)
(1) M-phase
(2) Interphase
(3) Leptotene
(4) S-phase
5. In G2 phase of cell cycle (Page 163, XI NCERT)
(1) RNA synthesis stops.
(2) DNA replicates.
(3) Deoxyribonucleotide synthesis begins.
(4) Tubulin protein synthesis takes place.
6. Given below is a schematic break-up of the phases/stages of the cell cycle
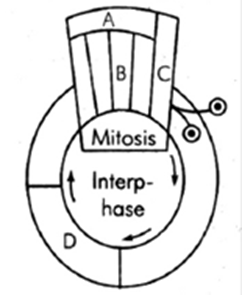
Which one of the following is the correct indication of the stage/phase in the cell cycle?
(1) B-Metaphase
(2) C-Karyokinesis
(3) D-Synthesis phase
(4) A-Cytokinesis
7. If the DNA content of an onion tip cell is 2C at the end of the M-phase, what would be its DNA content at the end of the S-phase? (Page 163, XI NCERT)
(1) C
(2) 2C
(3) 3C
(4) 4C
8. The centrioles replicate during: (Page 163, XI NCERT)
(1) G1 phase
(2) S phase
(3) G2 phase
(4) Early prophase
9. Which of the following is the correct sequence of events of interphase: -(Page 163, XI NCERT)
a. cells metabolically active
b. Duplication of the chromosome but chromosome number remains constant
c. M phased
d. Synthesis of protein [Tubulin]
(1) a→b→c→da→b→c→d
(2) a→d→b→ca→d→b→c
(3) a→b→d→ca→b→d→c
(4) a→c→d→ba→c→d→b
10. During cell cycle, events are under (Page 162, XI NCERT)
(1) Genetic control
(2) Metabolic control
(3) Cytoplasmic control
(4) Mitochondrial control
11. Which one of the following features differentiates G2 (Page 163, XI NCERT)
Which one of the following features differentiates G2 phase from G1 phase?
(1) Synthesis of proteins.
(2) 4C content of DNA.
(3) 2C content of DNA.
(4) Synthesis of RNA.
12. Cells in G0 phase:
(1) terminate the cell cycle
(2) exit the cell cycle
(3) enter the cell cycle
(4) suspend the cell cycle
13. During what phase in the cell cycle would you find the most DNA per cell?(Page 163, XI NCERT)
(1) G1
(2) G2
(3) S
(4) Prophase II
14. Consider the following four statements (I- IV) related to cell cycle, and select the correct option stating them as true (T) and false (F). (Page 162-164, XI NCERT)
I. Cell growth in terms of cytoplasmic increase is a continuous process.
II. Interphase is the phase of actual cell division.
III. The number of chromosomes doubles in S-phase.
IV. The cell that does not divide further exits G1-phase to enter a metabolically inactive stage.
Options:
I II III IV
(1) T F F F
(2) F T T T
(3) F F T T
(4) T F F T
15. Most of the organelle duplication occurs during which phase? (Page 171, Summary, XI NCERT)
(1) G1
(2) G2
(3) S
(4) M
16. When a cell stops growing, say due to shortage of nutrients, this will occur in which phase of the cell cycle?
(1) G0
(2) G1
(3) S
(4) G2
17. During which phase(s) of cell cycle, amount of DNA in a cell remains at 4C level if the inital amount is denoted as 2C? (PAGE 163, XI NCERT)
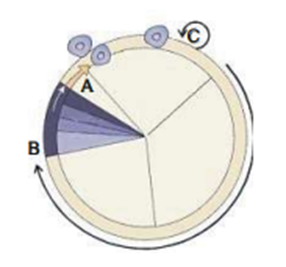
(1) G0 and G1
(2) G1 and S
(3) Only G2
(4) G2 and M
18. Identify the symbols A, B and C in the figure given below (Fig.10.1 Page 163, XI NCERT)
| A | B | C | |
| (1) | G0 | Prophase | Cytokinesis |
| (2) | Prophase | Metaphase | Telophase |
| (3) | G1 | S | G2 |
| (4) | Cytokinesis | Prophase | G0 |
1. (1)
2. (2)
3. (3)
4. (4)
19. Match the following column I with column II. (PAGE 163, 168-169, XI NCERT)
| Column I | Column II |
| A. Synapsis aligns homologous chromosomes | (i) Anaphase II |
| B. Synthesis of RNA and protein | (ii) Zygotene |
| C. Action of enzyme recombinase | (iii) G2 – phase |
| D. Centromeres do not separate, but chromatids move towards opposite poles | (iv) Anaphase I |
| (v) Pachytene |
(1) A-(ii) B-(i) C-(iii) D-(iv)
(2) A-(ii) B-(iii) C-(v) D-(iv)
(3) A-(i) B-(ii) C-(v) D-(iv)
(4) A-(ii) B-(iii) C-(iv) D-(v)
| Question | Answer |
| 1. | 1 |
| 2. | 1 |
| 3. | 3 |
| 4. | 2 |
| 5. | 4 |
| 6. | 3 |
| 7. | 4 |
| 8. | 2 |
| 9. | 3 |
| 10. | 1 |
| 11. | 2 |
| 12. | 4 |
| 13. | 2 |
| 14. | 1 |
| 15. | 1 |
| 16. | 2 |
| 17. | 4 |
| 18. | 4 |
| 19. | 2 |
1. Spindle fibres attach on to(PAGE 165, XI NCERT)
(1) Kinetochore of the chromosome
(2) centromere of the chromosome
(3) Kinetosome of the chromosome
(4) telomere of the chormosome
2. During cell division, the spindle fibres attach to the chromosomes at a region called (PAGE 165, XI NCERT)
1. chromocentre
2. kinetochore
3. centriole
4. chromomere
3. The figures below shows 3 phases of mitosis select the option given correct identification together with the correct event ? (Fig.10.2 c to e ;Page 166, XI NCERT)
1. C- Telophase-Nuclear envelope assembles around the chromosome clusters
2. B- Anaphase-Segregation of homologous chromosomes.
3. A- Prophase-Chromosomes get fully condensed.
4. C- Metaphase-Condensation of chromatin to form chromosome
4. Best stage to observe shape, size and number of chromosomes is (PAGE 165, XI NCERT)
1. interphase
2. metaphase
3. prophase
4. telophase
5. Which phase of mitosis is essentially the reverse of prophase in terms of nuclear changes?
(Page 165-166, XI NCERT)
1. S-phase
2. Anaphase
3. Telophase
4. Interphase
6. Which is the characteristic feature of metaphase? (Page 165, XI NCERT)
1. Spindle fibres attach to kinetochores of chromosomes.
2. Initiation of condensation of chromosomal material.
3. Chromosomes cluster at opposite spindle poles.
4. Disappearance of Golgi complexes, endoplasmic
reticulum, nucleolus, and the nuclear envelope.
7. Major event that occurs during anaphase of mitosis which brings about equal distribution of chromosomes is: (Page 165-166, XI NCERT)
1. Condensation of chromatin
2. Replication of genetic material
3. Splitting of centromere
4. Pairing of homologous chromosomes
8. Select the correct option with respect to mitosis. (PAGE 164-166, XI NCERT)
1. Chromatids start moving towards opposite poles in telophase
2. Golgi complex and endoplasmic reticulum are still visible at the end of prophase
3. Chromosomes move to the spindle equator and get aligned along equatorial plate in metaphase
4. Chromatids separate but remains in the centre of the cell in anaphase
9. Astral rays arise from
1. centriole
2. cytoplasm
3. chromatid
4. centromere.
10. When a cell is viewed under the microscope, it does not show golgi complex, endoplasmic reticulum, nucleolus, nuclear envelope in which stage of cell division? (Page 165,XI)
1. Early prophase
2. Late prophase
3. Interphase
4. Telophase
11. Which of the following does not occur during mitotic prophase?
(PAGE 164-165, XI NCERT)
(1) Disappearance of the nuclear envelope
(2) Chromosome condensation
(3) Migration of centrosomes towards the cell poles
(4) Synapsis of homologous chromosomes
12. In which stage of mitosis, shape of chromosomes is best studied?(Page 165, XI NCERT)
1. Prophase
2. Metaphase
3. Anaphase
4. Telophase
13. Chromosomes decondense into diffuse chromatin:(PAGE 166, XI NCERT)
(1) At the end of telophase
(2) At the beginning of prophase
(3) At the end of interphase
(4) At the end of metaphase
14. Which of the following options gives the correct sequences of events during mitosis? (PAGE 164-166, XI NCERT)
(1) Condensation → nuclear membrane disassembly → crossing over → Segregation → telophase
(2) Condensation → nuclear membrane disassembly → arrangement at equator → centromere division → Segregation → telophase
(3) Condensation → crossing over → nuclear membrane disassembly → Segregation → telophase
(4) Condensation → arrangement at equator → centromere division → Segregation → telophase
15. A stage in cell division is shown in the figure. Select the answer which gives correct
identification of the stage with its characteristics. (FIG.10.2(d), PAGE 166, XI NCERT)
1. Telophase – Nuclear envelope reforms, Golgi complex reforms
2. Late anaphase – Chromosomes move away from equatorial plate, Golgi complex not
present
3. Cytokinesis – Cell plate formed, mitochondria distributed between two daughter cells
4. Telophase – Endoplasmic reticulum and nucleolus not reformed yet
16. Initiation of the assembly of mitotic spindle and the complete disintegration of the nuclear envelope can be observed in respectively (Page 164-165, XI NCERT)
1. Prophase and anaphase I.
2. Metaphase and telophase.
3. Prophase and metaphase.
4. Metaphase and metaphase-I.
17. Congression of chromosomes is seen in (Heading 10.2.2, Page 165, XI NCERT)
1. Prophase
2. Metaphase
3. Anaphase
4. Telophase
18. Chromatin condensation and movement of duplicated centriole towards opposite pole can be observed during – (Page 164, XI NCERT)
1. Prophase
2. Metaphase
3. Anaphase
4. Telophase
19. The following cell undergoing mitosis, is at: (See figure 10.2, Page 165, XI NCERT)
1. Early prophase
2. Late prophase
3. Transition to metaphase
4. Early metaphase
20. During mitosis, endoplasmic reticulum and nucleolus begin to disappear at:(Page 165, XI NCERT)
1. Late metaphase
2. Early prophase
3. Late prophase
4. Early metaphase
21. During which phase(s) of cell cycle, amount of DNA in a cell remains at 4C level if the
inital amount is denoted as 2C? (PAGE 163, XI NCERT)
1. G0and G1
2. G1 and S
3. Only G2
4. G2 and M
22. Which of the following statements is True? (PAGE 166, XI NCERT)
(1) Cell plate represents the middle lamella between the walls of two adjacents cells
(2) At the time of cytokinesis, organelles like mitochondria and plastids get distributed between the daughter cells
(3) Cytokinesis in plant cell is centrifugal and takes place by cell-plate formation while animal cells by furrowing / cleavage and is centripetal
(4) All are correct
23. Metaphase I is different from mitotic metaphase as in the later case
(Page 165, 168-169, XI NCERT)
1. Two metaphasic plates are formed
2. Tetrads are arranged at the equator
3. Single metaphasic plate is formed
4. Homologous chromosomes get separated from each other
24. It begins with the simultaneous splitting of the centromere of each chromosome, is true for which stage (Page 165, 169, XI NCERTof Cell division)
1. Anaphase-I
2. Anaphase-II
3. Anaphase
4. More than one
| Question | Answer |
| 1. | 1 |
| 2. | 2 |
| 3. | 1 |
| 4. | 2 |
| 5. | 3 |
| 6. | 1 |
| 7. | 3 |
| 8. | 3 |
| 9. | 1 |
| 10. | 2 |
| 11. | 4 |
| 12. | 2 |
| 13. | 1 |
| 14. | 2 |
| 15. | 1 |
| 16. | 3 |
| 17. | 2 |
| 18. | 1 |
| 19. | 2 |
| 20. | 2 |
| 21. | 4 |
| 22. | 4 |
| 23. | 3 |
| 24. | 4 |
1. The furrow gradually deepens and ultimately joins in the centre dividing the cell cytoplasm into two. Here, the cell is (NCERT page number 166)
(1) Animal cell
(2) Plant cell
(3) Both A and B
(4) Only Root tip cells
2. Which of the following statements is True? (PAGE 166, XI NCERT)
(1) Cell plate represents the middle lamella between the walls of two adjacents cells
(2) At the time of cytokinesis, organelles like mitochondria and plastids get distributed between the daughter cells
(3) Cytokinesis in plant cell is centrifugal and takes place by cell-plate formation while animal cells by furrowing / cleavage and is centripetal
(4) All are correct
3. Mark the correct statement: ( Page 166, XI NCERT)
1 The stage between two successive meiotic division is generally long lived
2 In plant cells, wall formation starts in the centre of the cell and grows outward to meet the existing lateral walls
3 Meiosis results in conservation of specific chromosomes number of each species across generations in asexually reproducing organisms
4 Telophase – I can last for months or year
4. Identify the symbols A, B and C in the figure given below (Fig.10.1 Page 163, XI NCERT)
| A | B | C | |
| (1) | G0 | Prophase | Cytokinesis |
| (2) | Prophase | Metaphase | Telophase |
| (3) | G1 | S | G2 |
| (4) | Cytokinesis | Prophase | G0 |
1. (1)
2. (2)
3. (3)
4. (4)
5. Cytokinesis in animal cell takes place by _______; in _______ direction while in plant cell by _______; in _______ direction:
(1) Furrowing, centrifugal, cell plate, centripetal
(2) Furrowing, centripetal, cell plate, Centrifugal
(3) Cell plate, centrifugal, furrowing, centripetal
(4) Cell plate, centripetal, furrowing, centrifugal
6. The end of which of the following mark’s completion of Mitosis?
(NCERT page number 166)
1. Cytokinesis
2. Karyokinesis
3. Interkinesis
4. Telophase
7. Plant cells do not divided their cytoplasm by forming a furrow in cell membrane like animal cells rather they divide by cell plate because (PAGE 166, XI NCERT)
(1) Plant cell do not have centrioles
(2) Cell wall formation beings with formation of cell plate
(3) Cell plate represents middle lamella between the walls of two adjacent cells
(4) Plant cells are enclosed by a relatively inextensible wall
| Question | Answer |
| 1. | 1 |
| 2. | 4 |
| 3. | 2 |
| 4. | 4 |
| 5. | 2 |
| 6. | 1 |
| 7. | 4 |
1. The complex formed by a pair of synapsed homologous chromosomes is called (PAGE 168, XI NCERT)
1. equatorial plate
2. Kinetochore
3. bivalent
4. axoneme
2. Synapsis occurs between (PAGE 168, XI NCERT)
1. a male and a female gamete
2. mRNA and ribosomes
3. spindle fibres and centromere
4. two homologous chromosomes
3. In meiosis crossing over is initiated at
1. leptotene
2. zygotene
3. diplotene
4. pachytene
4. During gamete formation, the enzyme recombinase participates during
1. Metaphase-I
2. Anaphase-II
3. Prophase-I
4. Prophase-II
5. Reduction in the number of chromosomes occurs during (Page 169, XI NCERT)
1. Diplotene
2. Diakinesis
3. Metaphase I
4. Anaphase I
6. Which of the following is not a characteristic feature during mitosis in somatic cells
(1) Disappearance of nucleolus
(2) Chromosome movement
(3) Synapsis
(4) Spindle fibres
7. Bivalent align on the equator during (Page 168, XI NCERT)
1. Metaphase I of meiosis
2. Anaphase I of meiosis
3. Metaphase of mitosis
4. Anaphase of mitosis
8. Match the Column I with Column II – (Page 168, XI NCERT)
| Column-I | Column-II | ||
| 1. | Terminalization of chiasmata | A. | Zygotene |
| 2. | Synapsis | B. | Diplotene |
| 3. | Crossing over | C. | Metaphase I |
| 4. | Dissolution of synaptonemal complex | D. | Diakinesis |
| 5. | Best stage for the study of chiasmata | E. | Pachytene |
| 6. | Nuclear membrane and nucleolus disappear | ||
| 7. | Tetrads are arranged on equatorial line |
1. A – 2, B – 4,5, C – 7, D – 1,6, E – 3
2. A – 2, B – 3, C – 7, D – 1, 4, 6, E – 5
3. A – 2, B – 7, C – 3, D – 1, 4, 5, E – 6
4. A – 2, B – 1, C – 4, D – 5, 3, E – 6
9. Which of the following is characteristic of prophase I of meiosis I:-(Page 168, XI NCERT)
1. Synapsis in zygotene, genetically different chromatid are seen in pachytene
2. Exchange of genes in leptotene, genetically similar chromatids are seen in zygotene.
3. Chiasmata are present in metaphase
4. Splitting of centromere in anaphase-I
10. Following are the events occurs during meiosis : (Heading 10.4.1, Page 168, XI NCERT)
(A) Appearance of chiasmata
(B) Synapsis
(C) Assembly of meiotic spindle
(D) Use of recombinase enzyme
Choose the correct sequence :-
1. A→→B→→C→→D
2. B→→D→→A→→C
3. D→→C→→B→→A
4. B→→C→→A→→D
11. The exchange of segments of non-sister chromatids between chromosomes of a homologous pair termed as PAGE 168, XI NCERT
(1) transformation
(2) translocation
(3) crossing over
(4) chromosomal aberration
12. Crossing over takes place between which chromatids and in which stage of the cell cycle? Page 168, XI NCERT
1. Non-sister chromatids of non-homologous chromosomes at Zygotene stage of prophase I.
2. Non-sister chromatids of homologous chromosomes at Pachytene stage of prophase I.
3. Non-sister chromatids of homologous chromosomes at Zygotene stage of prophase I.
4. Non-sister chromatids of non-homologous chromosomes at Pachytene stage of prophase I.
13. Which of the following is not a characteristic of meiosis?
PAGE 167-169, XI NCERT
(1) It involves two stages of DNA replication one before meiosis-I and another before meiosis-II
(2) It involves recombination and crossing over
(3) Sister chromatids separate during anaphase- II
(4) Nuclear membrane disappears during prophase.
14. In meiosis crossing over is initiated at (PAGE 168, XI NCERT)
1. leptotene
2. Zygotene
3. diplotene
4. pachytene
15. Arrange the following events of meiosis in correct sequences
(PAGE 168, XI NCERT)
I. Crossing Over
II. Synapsis
III. terminalisation of chaismata
IV. Disapperance of nucleolus
(1) II, I, IV, III
(2) II, I, III, IV
(3) I, II, III, IV
(4) II, III, IV, I
16. In oocyte of some vertebrates, the stage of meiosis I that can last for months or years would be: (Page 168, XI NCERT)
1. Zygotene
2. Pachytene
3. Diplotene
4. Diakinesis
17. Which stage of meiosis – I is characterized by the appearance of recombination nodules? (Page 168, XI NCERT)
1. Diplotene
2. Zygotene
3. Diakinesis
4. Pachytene
18. “The synaptonemal complex is formed during _A_ stage and dissolves during _B_ stage”. Complete the above statement by choosing the correct option for A and B
A B
1. Diplotene Diakinesis
2. Leptotene Zygotene
3. Zygotene Diplotene
4. Pachytene Diplotene
19. Which of the following is not related to formation of bivalent? (Page 168, XI NCERT)
1. Synapsis
2. Recombinase
3. Zygotene
4. Synaptonemal complex
20. When synapsis is complete all along the chromosome, the cell is said to have entered a stage called ( PAGE 168, XI NCERT )
(1) Zygotene
(2) pachytene
(3) diplotene
(4) diakinesis.
21. Meiosis has evolutionary significance because it results in (PAGE 168 and 170, XI NCERT)
1. genetically similar daughters
2. four daughter cells
3. eggs and sperms
4. recombinations
22. The stage during which chiasmata becomes visible is ( Page 168, XI NCERT )
1. Pachytene
2. Diplotene
3. Diakinesis
4. Zygotene
23. The microtubules from the opposite poles of the spindle attach to the pair of homologous chromosomes in (Page 168, XI NCERT)
1. Metaphase – I
2. Prophase – I
3. Metaphase
4. Metaphase – II
24. The beginning of diplotene is recognized by : (Page 168, XI NCERT)
1. appearance of recombination nodules
2. Crossing over
3. Dissolution of synaptonemal complex
4. Appearance of chiasmata
25. The complex formed by a pair of synapsed homologous chromosomes is
(Page 168, XI NCERT)
1. Dyad
2. Tetrad
3. Univalent
4. Bivalent
26. Bivalent chromosomes clearly appear as tetrads during: (Page 168, XI NCERT)
1. Zygotene
2. Pachytene
3. Diplotene
4. Diakinesis
27. Which of the following stages of Meiosis I of Prophase I is not correctly matched with events occurring during that stage? Page 168, XI NCERT
| Stage | Event | |
| 1. | Zygotene | Pairing between homologous chromosomes |
| 2. | Pachytene | Crossing over between sister chromatids of homologous chromosomes |
| 3. | Diplotene | Tendency of recombined homologues to separate |
| 4. | Diakinesis | Terminalization of chiasmata |
28. The stage during which separation of the paired homologous chromosomes begins is ( PAGE 168, XI NCERT )
1. Pachytene
2. Diplotene
3. Diakinesis
4. Zygotene
29. Crossing over occurs just prior to (Page 168, XI NCERT)
1. Pachytene
2. Diplotene
3. Diakinesis
4. Zygotene
30. Each pole receives half the chromosome number of the parent cell, is true for which stage? (Page 171, Summary, XI NCERT)
1. Anaphase – II
2. Anaphase – I
3. Telophase-I
4. Telophase-II
31. Meiosis I: (PAGE 169, XI NCERT)
1. is always followed by interphase
2. is not followed by any period of rest
3. is followed by a period of interkinesis
4. is sometimes followed by interphase
32. Metaphase I is different from mitotic metaphase as in the later case
(Page 165, 168-169, XI NCERT)
1. Two metaphasic plates are formed
2. Tetrads are arranged at the equator
3. Single metaphasic plate is formed
4. Homologous chromosomes get separated from each other
33. Match the following column I with column II. (PAGE 163, 168-169, XI NCERT)
| Column I | Column II |
| A. Synapsis aligns homologous chromosomes | (i) Anaphase II |
| B. Synthesis of RNA and protein | (ii) Zygotene |
| C. Action of enzyme recombinase | (iii) G2 – phase |
| D. Centromeres do not separate, but chromatids move towards opposite poles | (iv) Anaphase I |
| (v) Pachytene |
1. A-(ii) B-(i) C-(iii) D-(iv)
2. A-(ii) B-(iii) C-(v) D-(iv)
3. A-(i) B-(ii) C-(v) D-(iv)
4. A-(ii) B-(iii) C-(iv) D-(v)
34. Select correct match (column I with column ll) (Page 168-169, XI NCERT)
Column l – Column ll
a. Bivalent as terad – (i) Diplotene
b. Chromatids separation – (ii) Telophase l
c. Terminalisation start phase – (iii) Anaphase ll
d. Nuclear membrane and nucleolus reappear – (iv) Pachytene
1 a(iv), b(iii), c(i), d(ii)
2 a(iv), b(iii), c(ii), d(i)
3 a(iii), b(iv), c(i), d(ii)
4 a(ii), b(iii), c(i), d(iv)
35. Alignment of bivalent chromosomes on the equatorial plate and splitting of centromeres occur respectively in which of the following stages of cell division? (Page 168-169, XI NCERT)
1. Anaphase I and anaphase II.
2. Metaphase II and anaphase I.
3. Metaphase I and anaphase II.
4. Pachytene and telophase I.
36. These given statements are related with specific phase of meiosis, select the unrelated statement with the phase given below.(Page 168-169, XI NCERT)
Statement Phase
1. The homologous chromosome – Anaphase I
separate, while sister
chromatids remain associated
at their centromere
2. The bivalent chromosomes align – Metaphase I
on the equatorial plate
3. Cytokinesis follows resulting in – Telophase I
the formation of tetrad of cells
4. Terminalisation of chiasmata – Final stage
of prophase
37. What is the correct sequence of the steps given here ? Also work out the process depicted in the steps. (PAGE 168-169, XI NCERT)
(i) Homologous chromosomes move toward opposite poles of the cell; chromatids do not separate
(ii) Chromosomes gather together at the two poles of the cell and the nucleare membranes reform
(iii) Homologous chromosomes pair and exchange segments
(iv) Homologous chromosomes align on a central plate
(v) The haploid cells separate completely
(1) The correct sequence is III→IV→I→II→VIII→IV→I→II→V and the process is meiosis-I
(2) The correct sequence is II→I→V→IV→IIIII→I→V→IV→III and the process is mitosis
(3) The correct sequence is IV→I→III→II→VIV→I→III→II→V and the process is meiosis-I
(4) the correct sequence is II→V→IV→I→IIII→V→IV→I→II and the process is mitosis
38. Chromosome number is reduced during meiosis because the process consists of:(PAGE 167, XI NCERT)
(1) Two cell divisions without any chromosome replication
(2) A single cell division without any chromosome replication
(3) Two cell divisions in which half of the chromosomes are destroyed
(4) Two cell divisions and only a single round of chromosome replication
39. Which of the following is not true for sister chromatids? (PAGE-168,169) XI NCERT
(1) They arise by replication during S phase
(2) They segregate from each other during each mitotic anaphase
(3) The usually contain identical versions of the same genetic information
(4) They segregate from each other during meiosis I
40. A reduction step during meiosis is important because:
(1) It returns the chromosome number to normal before fertilization
(2) There is a mechanism for this
(3) Only one copy of each chromosome is necessary
(4) Otherwise, chromosome copies would double each fertilization
| Question | Answer |
| 1. | 3 |
| 2. | 4 |
| 3. | 4 |
| 4. | 3 |
| 5. | 4 |
| 6. | 3 |
| 7. | 1 |
| 8. | 1 |
| 9. | 1 |
| 10. | 2 |
| 11. | 3 |
| 12. | 2 |
| 13. | 1 |
| 14. | 4 |
| 15. | 2 |
| 16. | 3 |
| 17. | 4 |
| 18. | 3 |
| 19. | 2 |
| 20. | 2 |
| 21. | 4 |
| 22. | 2 |
| 23. | 1 |
| 24. | 3 |
| 25. | 4 |
| 26. | 2 |
| 27. | 2 |
| 28. | 2 |
| 29. | 2 |
| 30. | 2 |
| 31. | 3 |
| 32. | 3 |
| 33. | 2 |
| 34. | 1 |
| 35. | 3 |
| 36. | 3 |
| 37. | 1 |
| 38. | 4 |
| 39. | 4 |
| 40. | 4 |
1.Match the following column I with column II. (PAGE 163, 168-169, XI NCERT)
| Column I | Column II |
| A. Synapsis aligns homologous chromosomes | (i) Anaphase II |
| B. Synthesis of RNA and protein | (ii) Zygotene |
| C. Action of enzyme recombinase | (iii) G2 – phase |
| D. Centromeres do not separate, but chromatids move towards opposite poles | (iv) Anaphase I |
| (v) Pachytene |
1. A-(ii) B-(i) C-(iii) D-(iv)
2. A-(ii) B-(iii) C-(v) D-(iv)
3. A-(i) B-(ii) C-(v) D-(iv)
4. A-(ii) B-(iii) C-(iv) D-(v)
2. Choose the odd one with respect to significance of meiosis (Page 170, XI NCERT)
1. Conservation of specific chromosome number of each species
2. Increases genetic variability
3. Able to regenerate part or whole of the organism
4. Introduces new combination of traits
3. Select correct match (column I with column ll)
Column l – Column ll
a. Bivalent as terad – (i) Diplotene
b. Chromatids separation – (ii) Telophase l
c. Terminalisation start phase – (iii) Anaphase ll
d. Nuclear membrane and nucleolus reappear – (iv) Pachytene
1. a(iv), b(iii), c(i), d(ii)
2. a(iv), b(iii), c(ii), d(i)
3. a(iii), b(iv), c(i), d(ii)
4. a(ii), b(iii), c(i), d(iv)
4. Alignment of bivalent chromosomes on the equatorial plate and splitting of centromeres occur respectively in which of the following stages of cell division?
1. Anaphase I and anaphase II.
2. Metaphase II and anaphase I.
3. Metaphase I and anaphase II.
4. Pachytene and telophase I.
5. During meiosis, the sister chromatids separate during:
(1) Anaphase II
(2) Anaphase I
(3) The S phase
(4) Synapsis
6. These given statements are related with specific phase of meiosis, select the unrelated statement with the phase given below.
Statement Phase
1. The homologous chromosome – Anaphase I
separate, while sister
chromatids remain associated
at their centromere
2. The bivalent chromosomes align – Metaphase I
on the equatorial plate
3. Cytokinesis follows resulting in – Telophase I
the formation of tetrad of cells
4. Terminalization of chiasmata – Final stage
of prophase
7. Identify the correct matched pair.
(1) Segregation-Metaphase ll
(2) Significance of meiosis-production of genetically similar cells
(3) Exchange of genetic material- DIakinesis
(4) Anaphase ll of meiosis-Centromeric division
8. What is the correct sequence of the steps given here ? Also work out the process depicted in the steps.
(i) Homologous chromosomes move toward opposite poles of the cell; chromatids do not separate
(ii) Chromosomes gather together at the two poles of the cell and the nucleare membranes reform
(iii) Homologous chromosomes pair and exchange segments
(iv) Homologous chromosomes align on a central plate
(v) The haploid cells separate completely
(1) The correct sequence is III→IV→I→II→VIII→IV→I→II→V and the process is meiosis-I
(2) The correct sequence is II→I→V→IV→IIIII→I→V→IV→III and the process is mitosis
(3) The correct sequence is IV→I→III→II→VIV→I→III→II→V and the process is meiosis-I
(4) the correct sequence is II→V→IV→I→IIII→V→IV→I→II and the process is mitosis
9. Chromosome number is reduced during meiosis because the process consists of:
(1) Two cell divisions without any chromosome replication
(2) A single cell division without any chromosome replication
(3) Two cell divisions in which half of the chromosomes are destroyed
(4) Two cell divisions and only a single round of chromosome replication
10. Which of the following is not true for sister chromatids?
(1) They arise by replication during S phase
(2) They segregate from each other during each mitotic anaphase
(3) The usually contain identical versions of the same genetic information
(4) They segregate from each other during meiosis I
11. By the end of Prophase II, chromosomes become ( PAGE 169, XI NCERT)
(1) Compact
(2) Loose
(3) Elongated
(4) Decondensed
12. It begins with the simultaneous splitting of the centromere of each chromosome, is true for which stage of Cell division. (Page 165, 169, XI NCERT)
1. Anaphase-I
2. Anaphase-II
3. Anaphase
4. More than one
13. A reduction step during meiosis is important because:
(1) It returns the chromosome number to normal before fertilization
(2) There is a mechanism for this
(3) Only one copy of each chromosome is necessary
(4) Otherwise chromosome copies would double each fertilization
14. Microtubules attach to kinetochore of sister chromatids during
(Heading 10.4.2, Page 169, XI NCERT)
1. Anaphase-I
2. Prophase-II
3. Metaphase-II
4. Anaphase-II
15. At anaphase-II, sister chromatids move towards opposite poles of the cell by:(Page 169, XI NCERT)
1. Contraction in spindle fibre attached to kinetochores
2. Shorterning of microtubules attached to kinetochores
3. Lengthening of microtubules attached to kinetochores
4. Relaxation in spindle fibre attached to kinetochores
16. When does Prophase II start usually? ( PAGE 169, XI NCERT)
(1) Chromosomes are fully elongated
(2) Before chromosomes are fully condensed
(3) Before chromosomes are fully elongated
(4) After chromosomes are fully elongated
| Question | Answer |
| 1. | 2 |
| 2. | 3 |
| 3. | 1 |
| 4. | 3 |
| 5. | 1 |
| 6. | 3 |
| 7. | 4 |
| 8. | 1 |
| 9. | 4 |
| 10. | 4 |
| 11. | 1 |
| 12. | 4 |
| 13. | 4 |
| 14. | 3 |
| 15. | 2 |
| 16. | 3 |