Physics is the study of laws of nature. Observable & Measurable quantities like Mass, Length, time, Force, velocity are called physical quantities. When measured, a physical quantity is expressed in terms of a multiple or sub – multiple of a standard value called a unit. The most common system of units which is in use is the international system of units.
S. I. UNITS:
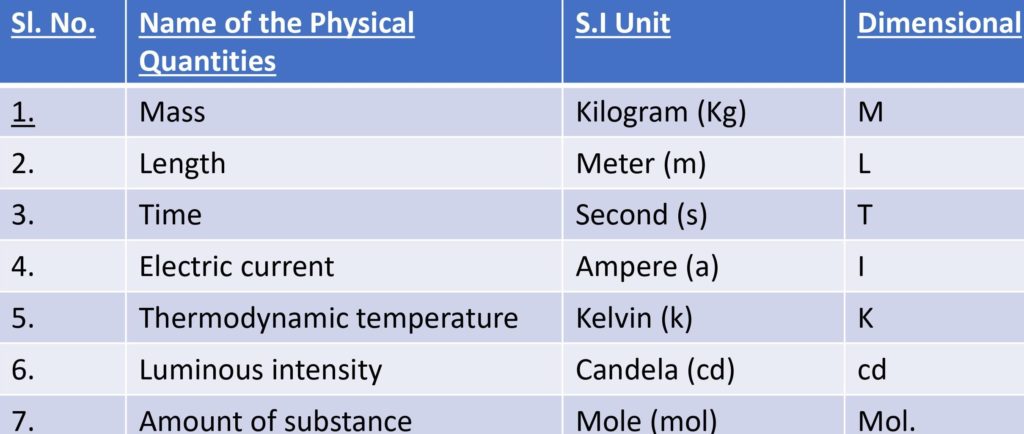
In the international system of unit, there are seven fundamental physical quantities and two auxiliary quantities as follows: -
(a) Fundamental Quantities: -
A set of minimum number of certain independent basis quantities necessary to describe all other physical quantities consistently and unambiguously are regarded as fundamental quantities.
(b) Auxiliary Quantities:
These quantities are dimensionless quantities helping us to understand other physical quantities in a better way.
- plane angle - radian (rad) ---
- solid angle - steradian (sr) ---
REQUIRMENT FOR A STANDARD UNIT
Invariability: - The standard unit must be invariable
Availability: The standard unit should be easily made available for comparing with other quantities.
DERIVED PHYSICAL QUANTITIES
Those quantities whose definitions are based on the use of some other fundamental physical quantities are called derived quantities e.g. area = length ×length; speed= length/time
DEFINATIONS OF FUNDAMENTAL UNITS IN S.I. :
Meter : It is the unit of the length. The distance travelled by light in vacuum in 1/299,792,458 Second is called 1 m.(1 meter is also equal to the length in which 1, 650, 763. 73 wave lengths (in Vacuum) of krypton-86 corresponding to the transition between 2p10 and 5d5 lie)
KILOGRAM: -
The mass of a particular cylinder made of platinum- iridium alloy kept at International Bureau of weight and measures is defined as 1 kg
Second: -
Cesium - 133 atom emits electromagnetic radiations of several wavelengths. A particular radiation is selected which corresponds to the transition between the two hyperfine levels of the ground state of Cs- 133. Each radiation has a time period of repetition of certain characteristics. The time duration in 9, 192, 631, 770 time period of the selected transition is defined as 1s.
Ampere: -
If two long straight wire with negligible cross – sections are placed parallel to each other in vacuum at a separation of 1m and equal electric current are established in the two in the same direction, the current in any of the wires is said to be 1 A .
Kelvin: -
The fraction 1/273.6 of the thermodynamic temperature of triple point of water is called 1k.
Mole: -
The amount that contains as many elementary entities (molecules or atoms if the substance is mono-atomic) as there are no of atoms on 0.012 kg of carbon- 12 is called a mole. This number (number of atoms in 0.012 kg of carbon – 12) is called Avogadro No. which is nearly equal to 6.02 × 1023 per mole
Candela: -
One candela is equal to the luminous intensity of a blackbody of a surface area m2placed at the temperature of freezing platinum and at a pressure of 101,325 N/m2 In the direction of perpendicular to its surface.
DEFINITION OF PLANE ANGEL
ACB is an arc of a circle as shown. θ is the angle subtended by the arc at 0, the centre of the circle. Let ACB be equal to l. R is the radius of the circle. . Total plane angle suspended at the centre 0=
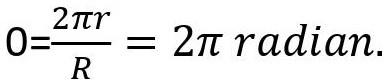
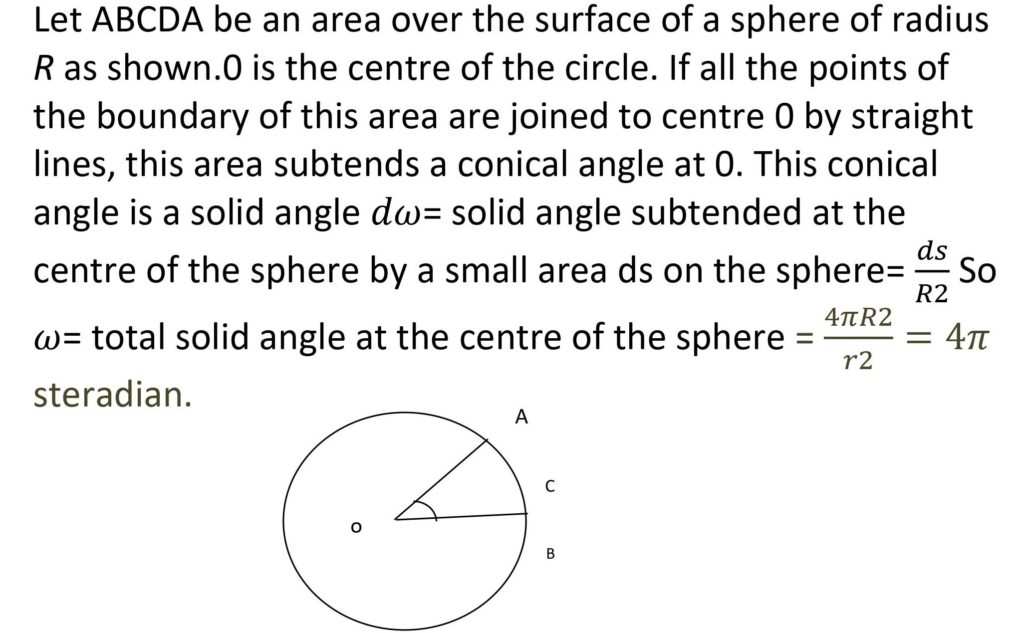
Definition of solid angle
DIMENTIONAL FORMULA:

USEFULLNESS OF DIMENTIONAL FORMULA
- (a) Conversion of unit from one system to another
- (b) Checking of dimensional accuracy of a physical equation: A dimensionally correct equation May or may not be correct. But a dimensionally wrong equation is wrong[Dimensional correctness means that the dimensions of each term in LHS & RHS of an equation are the same]
- (c) Derivation Of Physical laws.


… [Trackback]
[…] There you can find 82791 more Info on that Topic: eklabhyaclasses.com/blog/units-and-dimentions/ […]
… [Trackback]
[…] Find More on to that Topic: eklabhyaclasses.com/blog/units-and-dimentions/ […]
… [Trackback]
[…] Find More to that Topic: eklabhyaclasses.com/blog/units-and-dimentions/ […]
… [Trackback]
[…] Find More Information here on that Topic: eklabhyaclasses.com/blog/units-and-dimentions/ […]
… [Trackback]
[…] Here you will find 53207 more Information to that Topic: eklabhyaclasses.com/blog/units-and-dimentions/ […]
… [Trackback]
[…] Info to that Topic: eklabhyaclasses.com/blog/units-and-dimentions/ […]