1. Which group of vertebrates comprises the highest number of endangered species?
a) Reptiles
b) Birds
c) Mammals
d) Fishes
MCQ on Biodiversity & Conservation MCQ on Biodiversity & Conservation MCQ on Biodiversity & Conservation
2. The Indian wild ass is in the category of …… by Wildlife Protection Act of government of India.
a) Rare species
b) Endangered species
c) Endemic species
d) Vulnerable species
3. As estimated by Robert May, what is total number of species present on earth?
a) 3 million
b) 5 million
c) 7 million
d) 9 million
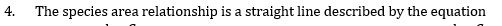
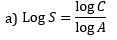
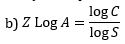
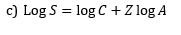
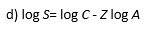
5. In India, hot spot area is found in
a) Eastern Himalaya
b) Tropical Andes
c) Madagascar
d) Meso –America
6. Hangul Project was started by government to save hangul (Cernus hanglu) in 1970. The sanctuary where it is started is
a) National Chambal sanctuary
b) Dachigam sanctuary
c) Corbett national park
d) Bandipur national park
7. Rivet Popper hypothesis explains the importance of
a) Species in an ecosystem
b) Birds in an ecosystem
c) Fishes in a pond ecosystem
d) None of the above
8. The term ‘Alpha diversity’ refers to
a) Genetic diversity
b) Community diversity
c) Species diversity
d) Diversity among the plants
9. Which endangered animal is the source of the world’s finest, lightest, warmest, and most expensive wool-the Shahtoosh?
a) Kashmiri goat
b) Chiru
c) Nilgai
d) Cheetal
10. Which one is an endangered species?
a) Cuscuta
b) Acacia nilotica
c) Nepenthes
d) Both (b) and (c)
MCQ on Biodiversity & Conservation
We would Like your Valuable Feedback
11. Land mass occupied by forest is
a) 40%
b) 22%
c) 30%
d) 17%
12. The greatest threat to genetic diversity in agricultural crops is
a) Extensive use of insecticides and pesticides
b) Extensive mixed cropping
c) Introduction of high yielding varieties
d) Extensive use of fertilizers
13. Which of the following species are restricted to an area?
a) Sibling species
b) Endemic species
c) Allopatric species
d) Sympatric species
14. More than 25% of the drugs are derived from the plants. What benefits does this described?
a) Aesthetic value
b) Ethical value
c) Indirect economic value
d) Direct economic value
15. Which of the following is conserved by ex situ conservation method?
a) All animals
b) All plants
c) Threatened animals and plants
d) None of the above
16. Soil erosion is prevented by
a) Deforestation
b) Afforestation
c) Reduction of CFCs production
d) Use of CNG in all transports
17. Many species like steller’s sea cow passenger pigeon have been driven to the brink of extinction. Which of the following describes this situation?
a) Over-exploitation by humans
b) Pollution
c) Habitat loss
d) Competition from introduced species
18. The number of species facing the threat of extinction worldwide is
a) 14,500
b) 14,000
c) 15,000
d) 15,500
19. In your opinion, which is the most effective way to conserve the plant diversity of an area?
a) By tissue culture method
b) By creating biosphere reserve
c) By creating botanical garden
d) By developing seed bank
20. Habitat loss and fragmentation, over exploitation, alien species invasion and co-extinction are causes for
a) Population explosion
b) Migration
c) Biodiversity loss
d) Pollution
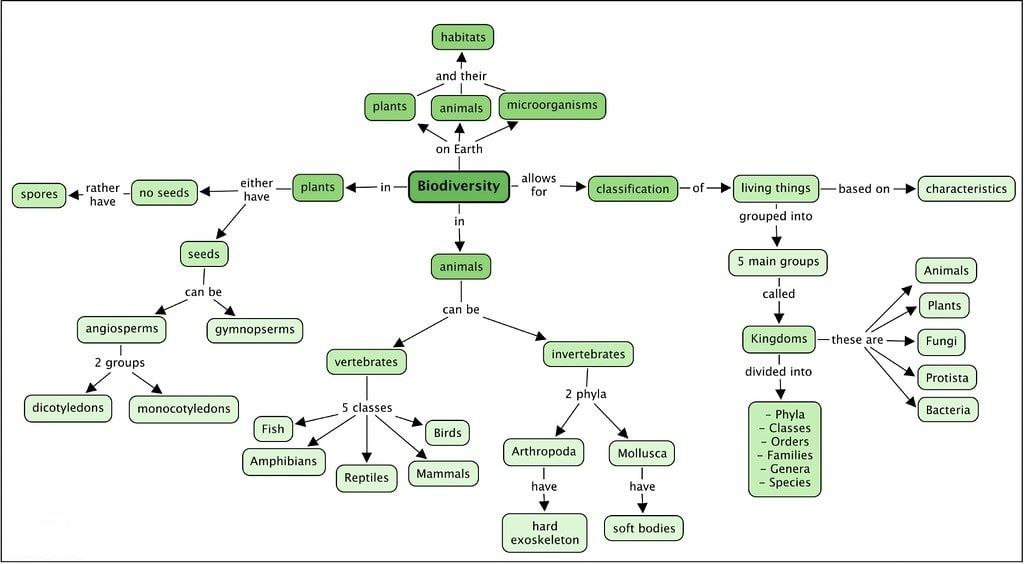
1.
(c) Threatened species in India include about 81 species of wild mammals, 30 wild birds, 15 reptiles and amphibians and many invertebrates.
2.
(b) Endangered species are those species, which are on the verge of extinction because of critically reduced number of individuals due to indiscriminate killing and due to drastic reduction in their habitats. Common endangered animals are Indian wild ass, Indian one –horned rhinoceros, etc
3.
(c) A more conservative and scientifically sound estimate made by Robert May, places the global species diversity at about 7 million
4.
5.
(a) Out of the 25 hotspots of the world, two are found in India. These are Western ghats and Eastern Himalayas and these extend to the neighboring countries also. These areas show high degree of endemism and area inhibited by a wide variety of flowering plants, swallow-tailed butterflies, amphibians, reptiles and mammals.
6.
(b) The Kashmir stag (Cervus elaphus hanglu) also called hangul, is a subspecies of Red Deer native to northern Pakistan and India. This deer lives in riverine forests, high valleys and mountains of the Kashmir valley and northern Chamba in Himachal Pradesh. In Kashmir, it’s found in Dachigam National Park.
7.
(a) Rivet popper hypothesis explains the importance of biodiversity for the survival of species. It was proposed by Paul Ehrlich
8.
(b) Alpha diversity refers to the diversity of organisms showing the same community for habitat. A combination of richness and equitability/evenness is used to represent diversity within a community or habitat.
9.
(b) Chiru is the source of Shahtoosh.
10.
(c)
Nepenthes is an endangered species of plant. Rauwolfia, Rhododendron, Psilotum,Ophioglossum are
some other endangered species of plants.
11.
(b) In the beginning of 20th century, about 30% of land mass in India was covered with forests and at the end of 20thcentury, it is reached by 19.4%.
12.
(c)
Genetic diversity is the diversity in the number and types of genes
as well as chromosomes present in different species and the variations
in the genes and their alleles in the same species. Introduction of
high yielding varieties is the greatest threat to genetic diversity
in agricultural crops.
13.
(b)
Endemic species are species which are restricted geographically in a particular area in a given time.
14.
(d)
Humans derives countless direct economic benefits from the nature like food, firewood, fibre, construction material, industrial products and products of medicinal importance. More than 25% of the drugs currently sold in the market worldwide are derived from the plants and 25000 species of the plants contributes to the traditional medicines used by native peoples around the world
15.
(c)
Ex situ strategy is the conservation of selected threatened plants and animal species.
Ex situ strategy is the conservation of selected threatened plant and animal species in
places outside their natural habitat, where the population is conserved
under stimulated conditions that closely resemble their natural habitats.
It includes, botanical gardens, zoological parks, wildlife safari,
gene banks, etc.
16.
(b)Afforestation or reforestation, i.e., growing of forest trees is most effective in controlling soil erosion. The Government of India has introduced the festival of ‘Van Mahotsav’. In this festival, planting of tress is done on open waste land.
17.
(a)
Excessive exploitation of a species, whether a plant or animal reduces
the size of its population, so that it becomes vulnerable to extinction.
Many marine fishes like whales population is declining around the world
because of over harvesting. Some commercially important species are likely
to become endangered
18.
(d) The number of species facing the threat of extinction worldwide is 15,500
19.
(b) Biosphere reserve is an in situ conservation method. Hence, it is the most effective way among the four for preserving genetic diversity by protecting wild population, traditional life style and domesticated plant genetic resource.
20.
(c) Loss of biodiversity occurs due to habitat loss, fragmentation over exploitation, alien species invasion and co-extinction.