(1) Which of the following hormone stimulates Gluconeogenesis (NCERT, Heading 22.2.8 Para 1 page 337)
1. Glucagon
2.Glucocorticoids
3.Insulin
4. Both 1 and 2
(2) Which of the following is incorrect about glucocorticoids (NCERT, page 337-338)
1. stimulate cellular uptake and utilization of amino acids
2. suppresses the immune response
3. Stimulate lipolysis and proteolysis
4. stimulate erythropoiesis
(3) Which of the following hormone is secreted by the adrenal cortex ( NCERT, page 336-337)
1. Adrenaline
2. Non- adrenaline
3. Catecholamines
4. None of these
(4) Diseases caused due to insufficiency of hormones include all except (Page 334-336, XI NCERT)
1. Cushing’s disease
2. Addison’s disease
3. Cretinism
4. Diabetes insipidus
(5) Which of the following is responsible for hyperglycemia ( XI NCERT, Heading 22.2.8 Para 1 page 336-337)
1. Glucagon
2. Glucocorticoids
3. Catecholamines
4. All of the above
(6) Match the follwing columns and select the correct option. (Page 334-336, 338 XI NCERT)
| Column I | Column II | ||
| (a) | Pituitary gland | (i) | Grave’s disease |
| (b) | Thyroid gland | (ii) | Diabetes mellitus |
| (c) | Adrenal gland | (iii) | Diabetes insipidus |
| (d) | Pancreas | (iv) | Addison’s disease |
| Options: | (a) | (b) | (c) | (d) |
| 1. | iii | ii | i | iv |
| 2. | iii | i | iv | ii |
| 3. | ii | i | iv | iii |
| 4. | iv | iii | i | ii |
(1) Which of the following is true about neural system (NCERT, Para 1, Page 331)
1. It provides point to point rapid coordination among organs
2. Coordination is fast and short lived
3. Response is very quick in it
4. All of the above
(2) Which of the following is true about Endocrine glands (NCERT, Heading 22.1, Para 1, Page 331)
(1) Ductless glands
(2) Secretion is hormones
(3) Pour its secretion into lymph and venous blood
(4) All of these
(3) The system which coordinate and regulate the physiological functions in the body is (NCERT, Para 1, Page 331)
(1) Nervous System and Excretory system
(2) Endocrine System and Circulatory system
(3) Nervous System and Endocrine System
(4) Excretory and Circulatory system
(4) Which of the following is true about Endocrine system (NCERT, Page 331)
(1) It is not directly connected with organs
(2) Response is slow
(3) coordinates through secretion of hormones
(4) All of the above
(5) Which one of the following statements is correct? (Page 331, XI NCERT)
1. Neurons regulate endocrine activity, but not vice versa.
2. Endocrine glands regulate neural activity, and nervous system regulates endocrine glands.
3. Neither hormones control neural activity nor do the neurons control endocrine activity.
4. Endocrine glands regulate neural activity, but not vice versa
(6) How many of the following organised endocrine glands are present in males? (NCERT, Heading 22.2, Para 1, Page 332)
Pancreas, Thymus, Adrenal, Testes, Kidney, GIT, Heart, Ovary, Pituitary, Thyroid
1. 10
2. 7
3. 6
4. 4
(1) Neurohypophysis store and release hormones which are actually synthesised by the hypothalamus and are transported axonally here. Which of the following hormones belong to this category? (Page 333, XI NCERT)
1. Glucocorticoid gonadotropins
2. FSH, LH
3. Oxytocin, Vasopressin
4. TSH, ACTH
(2) The basal part of diencephalon is ( XI NCERT, page 332)
1. Hypothalamus
2. Epithalamus
3. Thalamus
4. Both 2 and 3
(3) Which gland is under the direct neural regulation of hypothalamus? ( XI NCERT, page 332)
1. Pineal gland
2. Anterior pituitary gland
3. Posterior pituitary gland
4. Thyroid gland
(4) Which of the disease is likely to happen if an impairment affecting synthesis of ADH results in loss of water and dehydration ( XI NCERT, page 334)
(1) Diabetes Insipidus
(2) Diabetes Mellitus
(3) Both 1 and 2
(4) None of these
(5) Select the correct matching of hormone its source of
synthesis and function. (Page 333, XI NCERT)
| Hormone | Source | Function | |
| 1. | Glucagon | b-cells of pancreas | Increase blood glucose levels |
| 2. | Vasopressin | Hypothalamus | Increase diuresis |
| 3. | ACTH | Anterior lobe of pituitary | Stimulates synthesis and secretion of glucocorticoids |
| 4. | LH | Hypothalamus | Stimulates gonadal activity |
(6) Oxytocin and vasopressin synthesised in hypothalamus and reach to posterior pituitary by way of (Page 333, XI NCERT)
1. Anterior pituitary gland
2. Portal circulation
3. Blood vessels
4. Axons of hypothalamic neuron
(7) Sella Turcica is found (PAGE 333, XI NCERT)
1. in bones
2. in joints
3. nearby pituitary
4. nearby thyroid
(8) Read the following statement :- (Page 332, XI NCERT)
(a) The hypothalamus is the basal part of diencephalon
(b) Hypothalamus contains group of neurosecretory cells called ganglia which regulate the synthesis and secretion of pituitary hormone
(c) GnRH from hypothalamus stimulate the anterior pituitary to release gonadotrophins
(d) The posterior pituitary is under direct chemical regulation of the hypothalamus
How many of above statements are correct?
1. 4
2. 3
3. 1
4. 2
(9) Which of the following is a storage and release center for neurohormones? (Page 333, XI NCERT)
1. Anterior pituitary
2. Posterior pituitary
3. Adrenal medulla
4. Pineal
(10) Which one influences the activity of the kidney? (Page 334, 337, XI NCERT)
1. Vasopressin
2. Thyroxine
3. Vasopressin and aldosterone
4. Gonadotrophin
(11) Match the follwing columns and select the correct option. (Page 334-336, 338 XI NCERT)
| Column I | Column II | ||
| (a) | Pituitary gland | (i) | Grave’s disease |
| (b) | Thyroid gland | (ii) | Diabetes mellitus |
| (c) | Adrenal gland | (iii) | Diabetes insipidus |
| (d) | Pancreas | (iv) | Addison’s disease |
| Options: | (a) | (b) | (c) | (d) |
| 1. | iii | ii | i | iv |
| 2. | iii | i | iv | ii |
| 3. | ii | i | iv | iii |
| 4. | iv | iii | i | ii |
(1) Which of the following is caused because of the excess secretion of the GH? (XI NCERT, page 333)
1. Gigantism
2. Acromegaly
3. Dwarfism
4. Both 1 and 2
(2) A hormonal disorder that develops when pituitary gland produces too much growth hormone during adulthood is known as: ( Page 333, XI NCERT)
1. cretinism
2. gigantism
3. Conn’s syndrome
4. Acromegaly
(3) Given ahead is an incomplete table about certain hormones, their source glands and one major effect of each on the body in humans. Identify the correct option for the three blanks A, B and C. (PAGE 333-337, XI NCERT)
| Gland | Secretion | Effect on body |
| A Alpha cells of islets of Langerhans Anterior pituitary | Oestrogen B C | Maintenance of secondary sexual characters Raises blood sugar level Over secretion leads to gigantism |
Options :
A B C
1. Placenta Insulin Vasopressin
2. Ovary Insulin Calcitonin
3. Placenta Glucagon Calcitonin
4. Ovary Glucagon Growth hormone
Thyroid Gland Part II
(1) The thyroid gland is composed of (Heading 22.2.4 Para 1 page 334)
(1) Follicles
(2) Stromal tissues
(3) Follicular cells enclosing a cavity
(4) All of these
(2) Which of the following is true about thyroid gland? ( XI NCERT, page 334)
(1) It has 2 lobes
(2) It is present on either side of trachea
(3) both lobes are connected by a thin flap, Isthmus
(4) All of these
(3) The thyroid gland is composed of (XI NCERT, page 334)
(1) Follicles
(2) Stromal tissues
(3) Follicular cells enclosing a cavity
(4) All of these
(4) Find out the correct match for the following table.
Column-l Column-ll Column-lll
(i) Pituitary gland Growth hormone Acromegaly
(ii) Thyroid gland Thyroxine Exophthalmic goitre
(iii) Pituitary gland ADH Diabetes mellitus
1. (i) only
2. (i) and (ii)
3. (i) and (iii)
4. (ii) and (iii)
Heading 22.2.4, Page 334, 335
XI NCERT
(5) One of these pairs are not correctly matched (Page 337-338, XI NCERT)
1. Insulin – Raised blood sugar
2. Cretinism – Mental retardation
3. Grave’s Disease – swollen facial tissues
4. Parathyroid – Tetany
(6) Select the answer which correctly matches the endocrine gland with the hormone it secretes and its function/deficiency symptom: (PAGE 334, XI NCERT)
| Endocrine gland | Hormone | Function/deficiency symptom | |
| (1) | Posterior Pituitary | Growth Hormone (GH) | Oversecretion stimulates abnormal growth |
| (2) | Thyroid gland | Thyroxine | Lack of iodine in diet results in goitre |
| (3) | Corpus luteum | Testosterone | Stimulates spermatogenesis |
| (4) | Anterior pituitary | oxytocin | Stimulates uterus contraction during child birth |
1. (1)
2. (2)
3. (3)
4. (4)
(7) Thyroxine controls the metabolism of the following Macromolecules except ( XI NCERT, page 335)
(1) Carbohydrates
(2) Fats
(3) Proteins
(4) Nucleic acids
(8) Which of the following conditions is not linked to thyroid hormone? ( Page 334, 335, XI NCERT)
1. Cretinism
2. Goitre
3. Osteomalacia
4. Exophthalmic goitre
(9) Which of the following is likely to develop goitre? (Page 334, XI NCERT)
1. Thyroid gland that is producing too much parathormone
2. Circulating levels of thyrotropin are too low
3. There is an inadequate supply of iodine
4. The diet contains too much iodine
(10) Which of the following hormone regulates BMR of the body? (XI NCERT, page 334-335)
1. Thyroxine
2. Thyrocalcitonin
3. Adrenaline
4. Both 2. and 3.
(11) Graves disease is caused due to? (PAGE 335, XI NCERT)
1. hyposecretion of thyroid gland
2. hypersecretion of thyroid gland
3. hyposecretion of adrenal gland
4. hypersecretion of adrenal gland
(12) Dwarfism, pot belly and deaf-mutism are seen in which disease? (Page 334-335, XI NCERT)
1. Myxoedema
2. Cretinism
3. Grave’s disease
4. Basedow’s disease
(13) Identify the gland (a) and (b) shown below and select right option giving their number & function (Fig 22.3, Page 334-335 XI NCERT)
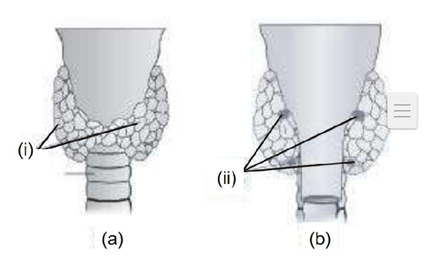
Gland Number Function
a (i) Thyroid 1 pair Promotes the bone deformation
b (ii) Thyroid 2 pairs Promotes the stunted growth of growing baby
c (i) Parathyroid 1 pair Increases the Ca+2level in bone
d (ii) Parathyroid 2 pairs Increase the Ca+2level in blood
1. 1
2. 2
3. 3
4. 4
(14) Diseases caused due to insufficiency of hormones include all except (Page 334-336, XI NCERT)
1. Cushing’s disease
2. Addison’s disease
3. Cretinism
4. Diabetes insipidus
(1) Which of the following is true about parathyroid glands? (NCERT, page 335)
(1) They are 4 in number
(2) Located on dorsal side of thyroid gland
(3) one pair parathyroid gland is present in each lobe of thyroid gland
(4) All of these
(2) Select the incorrect match with respect to hormones and respective deficiency disease (Page 333-335, XI NCERT)
1. PTH – Diabetes insipidus
2. Growth hormone – Dwarfism
3. Thyroid hormone – Cretinism
4. Adrenal cortex – Addison’s disease hormones
(3) Which hormone regulates the calcium level in our body? ( XI NCERT, page 335)
(1) Thyrocalcitonin
(2) Parathyroid hormone
(3) Thyroxine
(4) Both 1 and 2
(4) In a child of 15 years age, plasma calcium level is diagnosed below optimum level.Which organ is malfunctioning? (PAGE 335, XI NCERT)
1. Thyroid gland
2. Liver
3. Parathyroid
4. Posterior lobe of pituitary
(5) Parathyroid hormone works antagonistic with
(1) Thyrocalcitonin
(2) Thyroxine
(3) ACTH
(4) All of these
(6) A hormone that is antagonist to the parathyroid hormone is secreted from :
1. Thyroid
2. Adrenal cortex
3. Hypothalamus
4. Parathyroid itself
(7) If insufficient PTH is produced, the blood calcium level drops, resulting in ______. (Page 312, 335, XI NCERT)
1. reduced growth in childhood or parathyroid dwarfism
2. tetany, where the body shakes from continuous muscle contraction
3. osteoporosis
4. blood clotting
(8) Which of the following is incorrect with respect to parathyroid hormone (PTH)? (Page 335, XI NCERT)
1. Secretion of PTH is regulated by circulating levels of calcium ions.
2. PTH acts on bones and stimulates the process of bone mineralisation.
3. PTH stimulates the reabsorption of Ca+2 by renal tubules.
4. PTH increases the absorption of Ca+2 from digested food.
(9) Identify the incorrect statement: (PAGE 335 and 337, XI NCERT )
1. In males FSH regulates spermatogenesis
2. Thyroid gland produces T3 and thyroxine (T4) hormones
3. ACTH stimulates secretion of glucocorticoids
4. PTH is a hyperglycemic hormone
(10) The blood calcium level is lowered by the deficiency of ?
1. parathormone
2. thyroxine
3. calcitonin
4. Both 1. and 2.
(11) Which of the following symptom can not be expected, if there is tumour like growth in parathyroid glands? (Page 312 and 335, XI NCERT)
1. Tetany of muscle.
2. Increase in Ca++ level deposition of bones.
3. More tubular reabsorption of Ca++ from the nephric
tubule.
4. Both 1 and 2.
(12) Which of the following is not true about parathyroid hormone? (NCERT, Heading, 22.2.5 Para 2 page 335)
(1) It is a peptide hormone
(2) It stimulates resorption of bones
(3) It stimulates calcium absorption from renal tubules
(4) It stimulates calcium absorption from digested food
(1) Which of the following is true about glucocorticoids (PAGE 337, XI NCERT)
1. Regulate Cardio-vascular and kidney functions
2. Anti-inflammatory agent
3. stimulate erythropoiesis
4. All of the above
(2) A steroid hormone which regulates glucose metabolism is: (PAGE 337 and 340, XI NCERT)
1. cortisol
2. corticosterone
3. 11- deoxycorticosterone
4. cortisone
(3) A corticoid which is responsible for the electrolyte balance in our body is (NCERT, page 337)
1. Aldosterone
2. Adrenaline
3. Androgen
4. Both 1 and 3
(4) Glucocorticoids do not: (NCERT XI, Page 337)
1. Stimulate gluconeogenesis
2. Cause lipolysis
3. Cause proteolysis
4. Stimulate cellular uptake and utilization of amino acids
(5) A person with Addison disease ___________. (Page 336, XI NCERT)
1. is unable to replenish blood glucose levels under
stressful conditions
2. develops dramatically more male features
3. develops a rounded face and edema
4. has overgrowth of hands and face
(6) Identify the incorrectly matched pair: (Page 337, XI NCERT)
1. Growth hormone Increases blood glucose level
2. Thyroxin Supports erythropoiesis
3. Cortisol Promotes protein anabolism
4. Glucagon Stimulates gluconeogenesis
(7) Which set includes hormones that are involved in carbohydrate metabolism? (Page 336-337, XI NCERT)
1. Insulin, glucagon, epinephrine, calcitonin
2. Insulin, glucagon, epinephrine, cortisol
3. Insulin, glucagon, cortisol, melatonin
4. Insulin, glucagon, norepinephrine, melatonin
(1) Poor immunity of old people is because of the absence of which gland
(XI NCERT, page 335)
(1) Pineal gland
(2) Thymus
(3) Thyroid gland
(4) Parathyroid gland
(2) A gland called ‘Clock of ageing’ that gradually reduces and degenerates in ageing is (PAGE 335, XI NCERT)
1. thyroid
2. thymus
3. parathyroid
4. Pituitary
(3) Which of the following hormone is responsible for cell mediated immunity? (XI NCERT, page 335)
(1) Thyroxine
(2) adrenaline
(3) Thymosins
(4) parathyroid
(4) The immune responses in older people are weak due to the degeneration of: (Xl NCERT, Page 335, Section 22.2.6)
1. Thyroid
2. Pineal
3. Adrenal
4. Thymus
(5) Which of the following is incorrect about thymus gland (NCERT, page 335)
(1) lobular in structure
(2) located on ventral side of heart and aorta
(3) important for development of immune system
(4) It degenerates in old ages
(6) Which of the following hormone is responsible for humoral immunity?
(XI NCERT, page 335)
(1) Thyroxine
(2) Antibodies
(3) Thymosins
(4) parathyroid
(7) Which one of the following four glands is correctly matched with the accompanying description? (Page 335, XI NCERT)
1. Thyroid – hyperactivity in young children causes cretinism
2. Thymus – starts undergoing atrophy after puberty
3. Parathyroid – secrete parathormone which promotes movement of calcium ions from blood into bones during calcification
4. Pancreas – Delta cells of the Islets of Langerhans secrete a hormone which stimulates glycolysis
(1) Which of the following inhibits gastric secretion? (NCERT, Page 339)
1. Gastrin
2. Secretin
3. Cholecystokinin
4. Gastric inhibitory peptide
(2) Which of the following stimulates the secretion of HCl and pepsinogen? (NCERT, Heading 22.3, Para 2 page 339)
1. Gastrin
2. Secretin
3. Cholecystokinin
4. Gastric inhibitory peptide
(3) The hormones from the heart, kidney, and gastrointestinal tract respectively are: (Page 339, XI NCERT)
1. ANF, Rennin, Trypsin
2. ADH, Renin, GIP
3. ANF, Erythropoietin, CCK
4. GIP, CCK, Renin
(4) Identify the incorrect match: (Page 339, XI NCERT)
| Hormone Name | Source organ | Function | |
| 1. | Gastrin | Stomach | Stimulates gastric secretion |
| 2. | GIP | Duodenum | Inhibits gastric secretion |
| 3. | Secretin | Duodenum | Stimulates gastric secretion and motility |
| 4. | CCK-PZ | Duodenum mainly | Stimulates secretion of Pancreatic juice |
(5) Choose the incorrect statement ( Page 339, XI NCERT)
1. Thyroxine deficiency in adults causes Myxedema
2. PTH and TCT are responsible for maintaining the blood calcium level
3. Deficiency of aldosterone and cortisol causes Addison’s disease
4. Cholecystokinin promotes the release of bicarbonate ions from the pancreas and bile juice from the liver
(1) The binding of a hormone to its receptor leads to (NCERT, page 339-340)
1. formation of the hormone-receptor complex
2. leads to biochemical changes in the target tissue
3. affects target tissue metabolism
4. All of these
(2) Besides cAMP, which one of the following molecules acts as a “secondary messenger” in the biological system? (NCERT, Heading 22.4, page 340)
1. Ca+2
2. ATP
3. cDNA
4. CGTP
(3) Incorrect match with respect to hormone and its chemical nature is (Page 340, XI NCERT)
(1) Cortisol – Steroidal
(2) Thyroxine – Iodothyronine
(3) Glucagon – Steroidal
(4) Thyrocalcitonin – Proteinaceous
(4) Which of the following is an incorrect statement ( NCERT, Heading 22.4, Para 1 page 339)
1. Hormones bind to specific proteins located in the target tissues only.
2. Receptors for hormones can only be present on the cell membrane
3. Each receptor is specific to one hormone only
4. Nuclear receptors are intracellular receptors
(5) Which one of the following pairs of hormones are the examples of those that can easily pass through the cell membrane of the target cell and bind to a receptor inside it (mostly in the nucleus)? (PAGE 339-341, XI NCERT)
1. Insulin and glucagon
2. Thyroxin and insulin
3. Somatostatin and oxytocin
4. Cortisol and testosterone
(6) Identify A, B and C in the diagrammatic representation of the mechanism of hormone action. (Fig. 22.5 a, Page 340, XI NCERT)
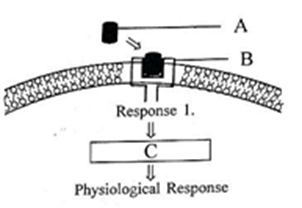
Select the correct option from the following:
1. A = Steroid Hormone; B = Hormone receptor Complex; C = Protein
2. A = Protein Hormone; B = Receptor; C = Cyclic AMP
3. A = Steroid Hormone; B = Receptor; C = Second Messenger
4. A = Protein Hormone; B = Cyclic AMP; C = Hormone-receptor Complex
(7) How many of the following hormones don’t enter the target cell?
Cortisol, Iodothyronine, Testosterone, Estradiol, FSH, Insulin, Glucagon
1. 4
2. 7
3. 3
4. 2
(8) Which of the following set of hormones can easily pass through the cell membrane of a target cell and bind to specific intracellular receptors? (Page 340, XI NCERT)
a. Placental progesterone
b. Aldosterone
c. Estrogen
d. Thyroxine
Mark the correct set:
1. b&c
2. a,b&c
3. a &c
4. a,b,c & d
(9) A hormone that has intracellular receptors would be
1. ACTH
2. ADH
3. Melatonin
4. Aldosterone
(10) The biomolecule that cannot act as a chemical messenger [hormone] is: (Page 340, XI NCERT)
1. Proteins
2. Steroids
3. Fatty acids
4. Carbohydrate
(11) Some hormones can act on their target cells through second messengers. Identify the one that does not: (Page 340, XI NCERT)
1. cortisol
2. adrenaline
3. FSH
4. Calcitonin
(12) What is correct for the hormone whose mechanism of action is shown in the given diagram? (page 340/341, Figure 22.5, XI NCERT)
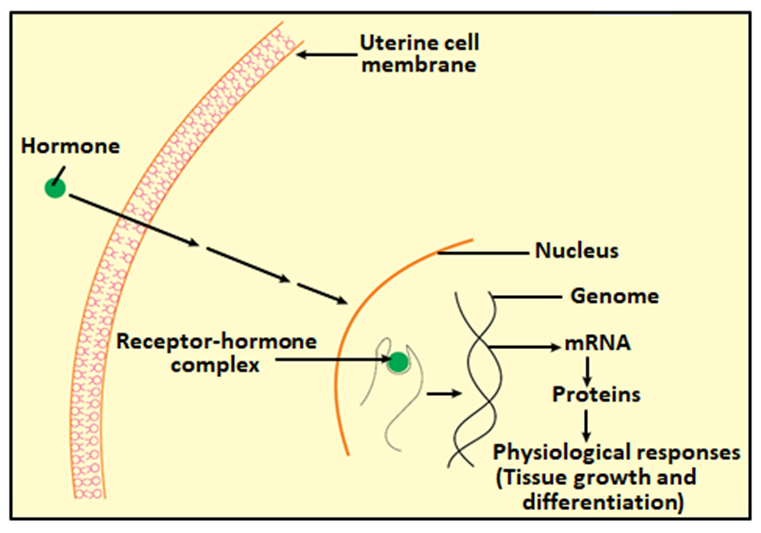
1. This hormone will most likely be synthesized by the neural cells of the hypothalamus
2. This hormone cannot be thyroxin or triiodothyronine
3. This hormone can be a derivative of cholesterol
4. This hormone will have an almost instantaneous onset of action
(13) Extracellular receptors must be required for the action of:
I. Oxytocin
II. Thyroxine
III. Epinephrine
IV. Glucagon
1. I, II, III & IV
2. I, IV only
3. I, III, IV
4. III & IV only
(14) How many of these hormones will interact with the membrane-bound receptor?
Thyroxin, epinephrine, progesterone, relaxin, estrogen:-
1. Three
2. Two
3. Five
4. One
(15) Chemically hormones are:- (Page 340, XI NCERT)
(1) Proteins, steroids & biogenic amines
(2) Proteins only
(3) Steroids only
(4) Biogenic amines only
Hormones of Heart, Kidney and Gastrointestinal Tract
(1) A peptide hormone which causes dilation of blood vessels and decreases blood pressure is (Page 339, XI NCERT)
1. Aldosterone
2. Adrenaline
3. Vasopressin
4. Atrial Natriuretic factor
(2) Which hormones do stimulate the production of pancreatic juice and bicarbonate? (Page 339, XI NCERT)
(1) Angiotensin and epinephrine
(2) Gastrin and insulin
(3) Cholecystokinin and secretin
(4) Insulin and glucagon
(3) Find out the correct match from the following table: (Heading 22.3, Page 339, XI NCERT)
| Column-I | Column-II | Column-III | |
| (i) | Heart | Atrial natriuretic factor | Decreases blood pressure |
| (ii) | Kidney | Erythropoietin | Formation of RBC |
| (iii) | Gastro-intestinal tract | Gastrin | Induces gastric secretion |
1. (ii) and (iii)
2. (i) and (iii)
3. (i) and (ii)
4. (i), (ii), and (iii)
(4) Match the following (Page 339, XI NCERT)
Column I Column II
(A) GIP (i) ↑↑ Crypts of Lieberkuhn
(B) Secretin (ii) ↑↑ HCO3HCO3 – secretion in pancreatic juice
(C) Cholecystokinin (iii) ↑↑ Brunner’s gland secretion
(D) Duocrinin (iv) ↑↑ Gastric juice secretion
(v) ↓↓ Gastric juice secretion
(vi) ↑↑ Contraction of gall bladder
A B C D
1. (v) (ii) (vi) (iii)
2. (ii) (v) (iii) (vi)
3. (v) (ii) (iii) (i)
4. (ii) (iv) (vi) (iii)
(5) Which of the following hormone is secreted from the intestinal mucosa and stimulates the release of enzymes in the pancreatic juice? (Page 339, XI NCERT)
1. Secretin
2. Cholecystokinin
3. Erterocrinin
4. Duocrinin
(6) Contraction in gall is bladder stimulated by : (Page 339, XI NCERT)
1. CCK
2. PZ
3. Secretin
4. Enterogastrin
(1) The glucose homeostasis in blood is maintained by ( NCERT, Heading 22.2.8 Para 1 page 338)
(1) Insulin
(2) Glucagons
(3) Both 1 and 2
(4) None of these
(2) Glucagon and insulin hormone can be distinguished based on (Page 337-338, XI NCERT)
1. Location of receptors i.e. intracellular or extracellular
2. Their source gland
3. Hepatocytes as target cells
4. Their role in the mechanism of maintaining glucose homeostasis
(3) Which of the following is true about Pancreas (NCERT, Heading 22.2.8 Para 1 page 337)
(1) Heterocrine gland
(2) Composite gland
(3) Endodermal in origin
(4) All of the above
(4) Given ahead is an incomplete table about certain hormones, their source glands and one major effect of each on the body in humans. Identify the correct option for the three blanks A, B and C. (PAGE 333-337, XI NCERT)
| Gland | Secretion | Effect on body |
| A Alpha cells of islets of Langerhans Anterior pituitary | Oestrogen B C | Maintenance of secondary sexual characters Raises blood sugar level Over secretion leads to gigantism |
Options :
A B C
1. Placenta Insulin Vasopressin
2. Ovary Insulin Calcitonin
3. Placenta Glucagon Calcitonin
4. Ovary Glucagon Growth hormone
(5) Select the correct statement about hormones and their actions. (PAGE 335-339, XI NCERT)
1. Parathyroid hormone increases K+ absorption of the body.
2. Insulin and glucagon helps to maintain blood sugar levels.
3. Old aged people have weak immunity due to increased activity of thymus.
4. Osteoporosis in women occurs due to increased levels of oestrogens.
(6) Which of the following is responsible for hyperglycemia ( XI NCERT, Heading 22.2.8 Para 1 page 336-337)
(1) Glucagon
(2) Glucocorticoids
(3) Catecholamines
(4) All of the above
(7) Which of the following statements regarding glucagon is false? (PAGE 337, XI NCERT)
1. It is secreted by αα-cells of Langerhans.
2. It acts antagonistically to insulin.
3. It decreases blood sugar level.
4. The gland responsible for its secretion is heterocrine gland
(8) Which of the following represents the action of insulin? (PAGE 337-338, XI NCERT)
1. Increases blood glucose level by stimulating glucagon production.
2. Decreases blood glucose level by forming glycogen.
3. Increases blood glucose level by promoting cellular uptake of glucose.
4. Increases blood glucose level by hydrolysis of glycogen.
(9) Which of the following hormones is incorrectly paired with its action? (Page 337, XI NCERT)
1. oxytocin–stimulates uterine contractions during childbirth
2. thyroxine–stimulates metabolic processes
3. insulin–stimulates glycogen breakdown in the liver
4. ACTH–stimulates the release of glucocorticoids by the adrenal cortex
(10) Which of the following is true about Islet of Langerhans (NCERT, Heading 22.2.8 Para 1 page 337)
(1) Known as exocrine pancreas
(2) 1 to 2% of the pancreatic tissue
(3) Secrete proteolytic enzymes
(4) secrete steroidal hormones
(11) Name a peptide hormone which acts mainly on hepatocytes, adipocytes and enhances cellular glucose uptake and utilisation. (PAGE 337-338, XI NCERT)
1. Insulin
2. Glucagon
3. Secretin
4. Gastrin
(12) Which one of the following pairs is incorrectly matched? (PAGE 332-338, XI NCERT)
1. Glucagon – Beta cells (source)
2. Somatostatin – Delta cells (source)
3. Corpus luteum – Relaxin (secretion)
4. Insulin – Diabetes mellitus (disease)
(13) Match the follwing columns and select the correct option. (Page 334-336, 338 XI NCERT)
| Column I | Column II | ||
| (a) | Pituitary gland | (i) | Grave’s disease |
| (b) | Thyroid gland | (ii) | Diabetes mellitus |
| (c) | Adrenal gland | (iii) | Diabetes insipidus |
| (d) | Pancreas | (iv) | Addison’s disease |
| Options: | (a) | (b) | (c) | (d) |
| 1. | iii | ii | i | iv |
| 2. | iii | i | iv | ii |
| 3. | ii | i | iv | iii |
| 4. | iv | iii | i | ii |
(14) Which of the following hormone is responsible for hypoglycemia (NCERT, Heading 22.2.8 Para 1 page 337)
(1) Insulin
(2) Glucagon
(3) Growth hormone
(4) Both 1 and 3
(15) The condition of prolonged hyperglycemia leads to ( NCERT, page 298 and 338)
(1) Diabetes Insipidus
(2) Diabetes mellitus
(3) Glycosuria
(4) Both 2 and 3
(16) Identify the hormone: (Page 337-338, XI NCERT)
I. It favors glycogenesis
II. It favors fat synthesis and deposition
III. It favors protein anabolism
1. Cortisol
2. Insulin
3. Growth hormone
4. Adrenaline
(17) Which of the following acts on the endocrine part of the pancreas?
1. Gastrin
2. Secretin
3. Cholecystokinin
4. None of these