MCQ on Cell Cycle and Cell Division MCQ on Cell Cycle and Cell Division
1. The second meiotic division leads to
a) Separation of sex chromosomes
b) Fresh DNA synthesis
c) Separation of chromatids and Centromere
d) Separation of homologous chromosomes
2. In meiosis, chromosome number becomes
a) Half of its parent chromosome
b) Same as that of parent chromosome
c) One fourth of its parent chromosome
d) None of the above
3. Consider the following statements about plant cytokinesis
I. It usually occurs by cell plate method
II. The spindle usually persists during cytokinesis
III. Cell plate grows centrifugally
Which of the statements given above are correct?
a) I and II
b) I and III
c) II and III
d) I, II and III
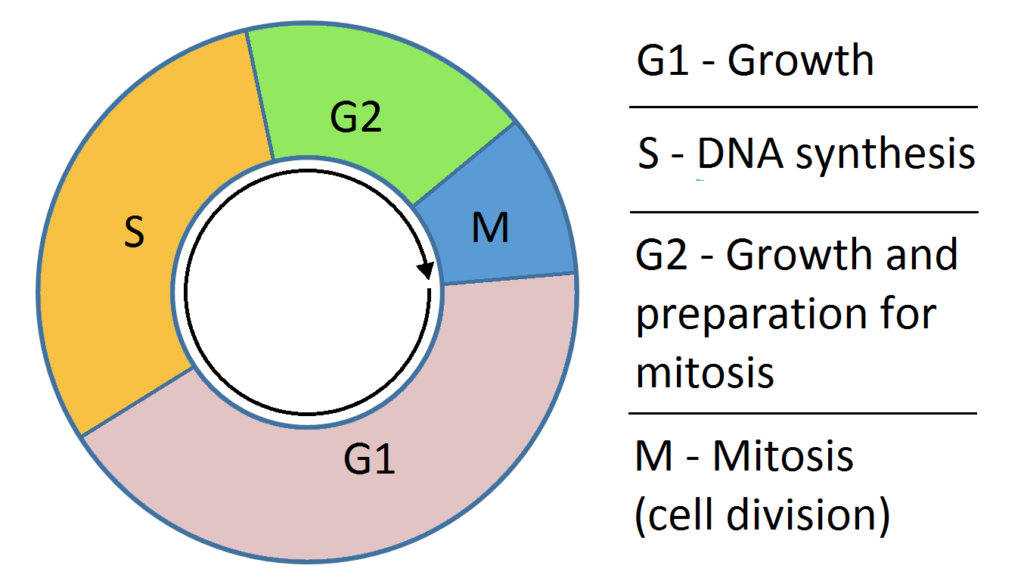
4. I. …A… phase corresponds to the interval between mitosis and initiation of DNA replication
II. In animal cells, during the …B… phase, DNA replication begins in the nucleus and the centriole duplicates in the cytoplasm
III. During the …C… phase, proteins are synthesized for the preparation of mitosis, while cell growth continues
Identify the blanks (A-C) to complete the given statements (I-III) with reference to NCERT textbook
a) A-G2, B-S, C-G1
b) A-S, B-G2, C-G1
c) A-S, B-G1, C-G2
d) A-G1, B-S, C-G2
5. Select the matched ones.
I . S-phase - DNA replication
II. Zygotene - Synapsis
III. Diplotene - Crossing over
IV. Meiosis - Both haploid and diploid cells
V G2-phase - Quiescent stage
a) I and II only
b) III and IV only
c) III and V only
d) I,III and V only
6. Which type of cell division helps in regeneration of cells?
a) Mitosis
b) Amitosis
c) Meiosis
d) Karyokinesis
7. Which of the following statement(s) is/are not correct about meiosis?
I. Meiosis involves pairing of homologous chromosomes and recombination between them
II. Two diploid cells are formed at the end of meiosis-II
III. Meiosis involves two sequential cycles of nuclear and cell division called meiosis-I and meiosis-II, but only a single cycle of DNA replication
IV. Meiosis-I is initiated after the parental chromosome replication which produce identical sister chromatids at the S-phase
The correct option is
a) I and III
b) II only
c) II and III
d) I, II, III and IV
8. Choose the correct statements regarding cell cycle
I. Interphase is called the resting phase
II. Interphase is the time during which the cell is preparing for division
III. The interphase is divided into phases, i.e.,G1, S and G2-phase
IV. Interphase represents the phase between the two successive M-phases
The option with correct statements is
a) I and IV
b) II and III
c) I and III
d) I, II, III and IV
9. Crossing over occurs during
a) Leptotene
b) Diplotene
c) Pachytene
d) Zygotene
MCQ on Cell Cycle & Cell Division
We would Like your Valuable Feedback
10. During meiosis, the alleles of the parental pair separate or segregated from each other. How many allele(s) is/are then transmitted to a gamete?
a) Four
b) Two
c) Six
d) One
11. The phragmoplast is organized at the
a) Beginning of anaphase
b) End of anaphase
c) Beginning of telophase
d) End of telophase
12. The morphology of chromosomes can be studied most easily in
a) Prophase
b) Metaphase
c) Anaphase
d) Telophase
13. Identify the correct stage of mitosis by viewing the diagram carefully?
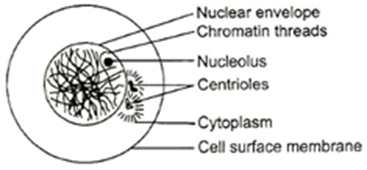
a) Interphase
b) Prophase
c) Metaphase
d) Anaphase
14. The number of chromosomes becomes half in
a) Anaphase-I
b) Anaphase-II
c) Telophase-I
d) Telophase-II
15. In which of the following phase of cell cycle, mitotic division got arrested?
a) G2-phase
b) G0-phase
c) S-phase
d) M-phase
16. Which of the following phase of cell cycle is also known as the resting phase?
a) G1-phase
b) M-phase
c) S-phase
d) Interphase
17. Differentiated cell remains at which stage?
a) G1
b) G2
c) G0
d) M
18. The process of cytokinesis refers to the division of
a) Nucleus
b) Chromosomes
c) Cytoplasm
d) None of these
19. Choose the correct combination of options to select the correct statement for prophase
I. Chromosomal material condenses to form compact mitotic chromosomes
II. The assembly of mitotic spindle is initiated by the microtubules
III. Cells do not show organelles when viewed under the prophase
IV. The nucleolus or nucleoli degenerate completely
a) I only
b) II and III
c) I and II
d) All of these
20. Which of the following event distinguishes prophase-I of meiosis from prophase of mitosis?
a) Nuclear membrane breaks down
b) Chromosomes become visible
c) Homologous chromosomes pair up
d) Spindle forms
1 (c)
Meiosis first is allowed by second meiotic division, which is essentially a mitotic division and is referred as mitotic. In anaphase-II of meiosis-II, the chromosome and centromere divide. The sister chromatids separate and move towards opposite pole.
2 (a)
In meiosis (meiotic-I), chromosome number becomes half to that of parent chromosome.
3 (d)
Plant cytokinesis usually occurs by cell plate method. The spindle usually pesists during cytokinesis. Central part of spindle grows in size and forms an interdigited complex called phragmoplast. Cell plate grows centrifugally
4 (d)
A-G1, B-S, C-G2.
Post reproductive stage of a cell includes cell growth. The term cell growth is used in the contexts of cell development and cell division. As we are concerned about growth (development) only, it refers to the growth of cell that is to increase in cytoplasmic and organelle volume that is in G1-phase
S-phase is the sub-phase between G1-phase and G2-phase, during which DNA synthesis or replication takes place.
In animal cells, during the S-phase, DNA replication begins in the nucleus and the centriole duplication in the cytoplasm. The amount of DNA per cell doubles in the nucleus. If the initial amount of DNA is denoted as 2C, then it increases to 4C. However, there is no increase in the chromosome number
5 (a)
S or synthetic phase marks the period during which DNA synthesis or replication takes place. During this phase, the amount of DNA per cell doubles.
The second stage of prophase-I is called zygotene. During this stage, chromosomes start pairing together and this process of association is called synapsis. Such paired chromosomes are called homologous chromosomes. Synapsis is accompanied by the formation of a complex structure called synaptonemal complex.
6 (a)
Mitosis is one of the types of cell division, which helps in regeneration. Because it keeps all the somatic cells of an organism genetically similar, so that they are able to regenerate a part or whole of the organism
7 (b)
During meiosis, four haploid cells are produced by reductional division from a single diploid cell. Parent cell contains replicated chromosomes, but the daughter cells contain un replicated chromosomes
8 (d)
The interphase, as called the resting phase, is the time during which the cell is preparing for division by undergoing both cell growth and DNA replication.
It is the phase between two successive M-phases
The interphase is divided into three further classes
G1-phase (Gap 1), S-phase (synthesis) and G2-phase (Gap 2)
9 (c)
Crossing over occurs during pachytene or thick thread or pachynema substage of prophase-I of meiosis. During this stage, an exchange of portions of chromatids between homologous chromosomes occur. At chiasma, the chromatids break re-join in such a way that sections are exchanged.
10 (d)
Out of two alleles present at the same locus of two chromosomes of a homologous pair, one is transmitted to a gamete as the later receive one chromosome of a homologous pair.
11 (b)
In plant cells, cytokinesis occurs by cell plate formation. A number of elements called phragmoplasts are derived from ER and Golgi body. These elements line up at equator during anaphase and later fuse to form cell plate.
12 (b)
During metaphase, the nuclear envelope disintegrates and the chromosomes are spread through the cytoplasm of the cell. Condensation of chromosomes is completed and it can be observed under the microscope. At this stage, the morphology as well as the number of chromosomes can be easily studied
13 (a)
Interphase has variable duration. During this period, the DNA of chromosomes replicates. Chromosome material is in the form of very loosely coiled threads called chromatin. Centrioles already have replicated
14 (a)
During anaphase-I, the number of chromosomes become half.
15 (b)
G0-phase.
Some cells that do not divide further, exit G1-phase and enter an inactive stage called quiescent stage (G0) of the cell cycle. Cells in this stage remains metabolically active but no longer proliferate unless called on to do so depending on the requirement of the organism
16 (d)
The interphase is also called the resting phase. It is the time during which the cell gets prepared for division by undergoing both cell and DNA replication in an orderly manner
17 (c)
The cells, which do not divide further, do not proceed beyond the G1-phase and start undergoing differentiation into specific type are said to be in G0-phase.
18 (c)
Division of cytoplasm is called cytokinesis (Gr. kitos=cell; kinesis=movement).
19 (d)
At the end of prophase, several characteristic events can be observed. Chromosomal material condenses to form compact mitotic chromosomes. Two chromatids attach together to form chromosomes
Assembly of mitotic spindle is initiated by, microtubules (proteinaceous components) of the cell cytoplasm. When observed under the microscope cells at the last stage of prophase, do not shows cell organelles like, Golgi complexes, endoplasmic reticulum, nucleolus and the nuclear envelope
20 (c)
| Prophase-I of Meiosis | Prophase of Mitosis |
| Prophase-I is very long and elaborate, comprising 5 sub-phases Prophase chromosomes appear double from the very start There is no pairing of homologous Chromosomes, hence no chance of crossing over | Prophase is relatively very short and simple Prophase-I chromosome do not look double in the beginning Homologous chromosomes pair and often undergo crossing over in prophase-I |
[…] DPP-1 […]
… [Trackback]
[…] Read More to that Topic: eklabhyaclasses.com/blog/mcq-on-cell-cycle-and-cell-division/ […]
… [Trackback]
[…] Read More Information here to that Topic: eklabhyaclasses.com/blog/mcq-on-cell-cycle-and-cell-division/ […]
… [Trackback]
[…] Find More Info here on that Topic: eklabhyaclasses.com/blog/mcq-on-cell-cycle-and-cell-division/ […]
… [Trackback]
[…] Information to that Topic: eklabhyaclasses.com/blog/mcq-on-cell-cycle-and-cell-division/ […]