MCQ on Cell Cycle and Cell Division MCQ on Cell Cycle and Cell Division
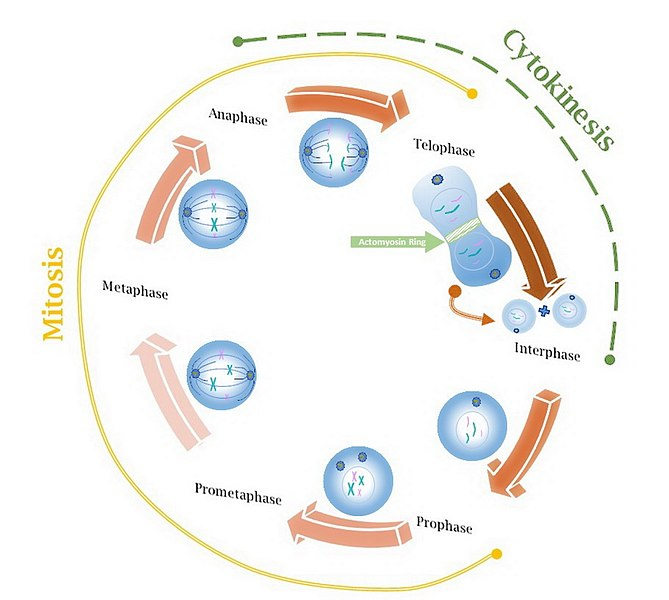
1. During mitosis, number of chromosomes gets
a) Change
b) No change
c) May be change if cell is mature
d) May be change if cell is immature
2. I. Chromosomes cluster at opposite spindle poles their identity is lost as discrete elements
II. Nuclear envelope assembles around the chromosome clusters
III. Nucleolus, Golgi complex and ER reform
Above features indicates which phase of mitosis
a) Anaphase
b) Telophase
c) Cytokinesis
d) S-phase
3. What would be the change in the chromosome number, during S-phase?
a) No change
b) The number of chromosome doubles
c) The number of chromosome doubles only in case of diploid cell
d) The number of chromosome doubles only in case of haploid cell
4. Arrange the following events of meiosis in a correct sequence and choose the correct option
I. Terminalisation
II. Crossing over
III. Synapsis
IV. Disjunction of genomes
a) IV, III, II and I
b) III, II, I and IV
c) II, I, IV and III
d) I, IV, III and II
5. What is the approximate percentage duration of cell cycle that comes under interphase in humans?
a) 99%
b) 95%
c) 25%
d) 5%
6. Which of the following stage of meiosis is responsible for deciding genetic constitution of gametes?
a) Metaphase-II
b) Anaphase-II
c) Metaphase-I
d) Anaphase-I
7. …A…. mitotic cell division is only seen in the diploid somatic cells, while the …B… can show mitotic divisions in both haploid and diploid cells.
Identify A and B form the options given below
a) A-Animals; B-plants
b) A-Plants; B-animals
c) A-Bacterial; B-viruses
d) None of these
8. Given diagram indicates which of the following phase of mitosis? Choose the correct option

a) Interphase
b) Prophase
c) Metaphase
d) Anaphase
9. In meiosis, the chromosome number
a) Reduces by half
b) Increase by twice
c) Increase by four times
d) Reduces by one-fourth
MCQ on Cell Cycle & Cell Division
We would Like your Valuable Feedback
10. The phase between two successive M-phase is called
a) S-phase
b) G1-phase
c) G2-phase
d) Interphase
11. At the end of meiosis-II, number of haploid cells formed are
a) Two
b) Four
c) Eight
d) None of these
12. The transition between meiosis-I and meiosis-II is
a) Interkinesis
b) Cytokinesis
c) Diakinesis
d) Karyokinesis
13. Synapsis occurs between
a) A male and a female gamete
b) mRNA and ribosomes
c) Spindle fibres and centromere
d) Two homologous chromosomes
14. In which stage of cell division, chromosomes are most condensed?
a) Prophase
b) Metaphase
c) Anaphase
d) Telophase
15. Which of the protein is found in spindle fibre?
a) Tubulin
b) Albumin
c) Mucin
d) Haemoglobin
16. Which of the following events occurs during G1-phase?
a) DNA replication
b) Growth and normal function of cell
c) Mutation
d) Fertilization
17. Select the correct statements regarding S-phase of interphase
I. Occurs between G1 and G2
II. DNA replication begins in the nucleus
III. Centrioles duplicate in the cytoplasm
IV. As DNA is doubled, number of chromosomes also doubles
The option with correct statements is
a) IV and III
b) I, II, III and IV
c) II, III and IV
d) I, II and III
18. A material, which arrests cell division, is obtained from
a) Crocus
b) Colchicum
c) Dalbergia
d) Chrysanthemum
19. During cell division, sometimes there will be failure of separation of sister chromatids. This event is called
a) Interference
b) Complementation
c) Non-disjunction
d) Coincidence
20. I. The cells that do not divide further, exit G1-phase to enter an inactive stage called …A… phase of the cell cycle
II. The cells that are in G2-phase definitely continue with the …B… phase.
Identify A and B to complete the given NCERT statements
a) A-G0; B-S
b) A-S; B-G0
c) A-M; B-G0
d) A-G0; B-M
1 (b)
Mitosis was first observed by Strasburger and termed by W Flemming. During mitosis, chromosome number remain same in the daughter cells. During meiosis (reduction division), the chromosome number reduced to half in the daughter cells.
2 (b)
Telophase is the reverse stage of prophase. During this phase, the cytoplasmic viscosity decreases and the two chromosome groups reorganize themselves into nuclei. A nucleae envelope appears outside the nucleoplasm collected in the area of chromatin. Spindle fibres disappear around the poles and Golgi complex and endoplasmic reticulum are reformed
3 (a)
During S-phase, there is no increase in the chromosomes number. If the cell has diploid or 2n number of chromosomes at G1, even after S-phase the number of chromosomes remains the same, i.e., 2n
4 (b)
The correct sequence is
Synapsis → crossing over → terminalisation → disjunction of genomes
5 (b)
The interphase takes approximate 75-95% of the entire generation time
6 (d)
The paternal and maternal chromosomes of each homologous pair segregates during anaphase-I. Although, both (maternal and paternal) chromosomes of a homologous pair have the genes for the same traits, either chromosome of a pair may carry different alleles of the same genes. Therefore, in anaphase-I, homologous chromosomes introduces genetic variability
7 (a)
A-Animals; B-Plants
8 (a)
At the onset of anaphase, each chromosome arranged at the metaphase plate is split simultaneously and the two daughter chromatids, now referred to as chromosomes of the future daughter nuclei, begin their migration towards the two opposite poles. As each chromosome moves away from the equatorial plate, the centromere of each chromosome is towards the pole and hence at the leading edge, with the arms of the chromosome trailing behind. Thus, anaphase stage is characterized by the following key events
Centromeres split and chromatids separate
Chromatids move to opposite poles
9 (a)
After meiosis, the chromosomes get reduce by half, producing haploid cells. The sperm and the egg are haploid cells and when they fuse during fertilization, they produce diploid original
10 (d)
The phase between two successive M-phases is called interphase.
The M-phase represents the phase when the actual cell division or mitosis occurs and the interphase represents the phase between two successive M-phases. It is significant to note that in the 24hour average duration of cell cycle of a human cell, cell division proper lasts for only about an hour. The interphase lasts more than 95% of the duration of cell cycle
11 (b)
Meiosis starts with one diploid containing copies of chromosome, one from mother and one from father. The cell divides twice, producing up to four haploid cells containing one copy of each chromosome
12 (a)
Interkinesis is the transition stage between meiosis-I and meiosis-II.
13 (d)
In zygotene of prophase-I, homologous chromosomes pair up. This process is called synapsis. One chromosome of the pair is from the male parent and other from the female parent.
14 (b)
In metaphase, chromosomes are shortest and show maximum condensation. Chromosomes are arranged at equatorial metaphasic plate. Structure, size and number of chromosomes are best studied at metaphase.
15 (a)
Microtubules are mainly composed of tubulin protein. These are found only in eukaryotic cellular structures like cilia, flagella, centriole, basal body, spindle fibre, etc.
16 (b)
G1-phase is called as pre-synthetic phase or post-mitotic phase. It is the longest phase of cell cycle. In G1-phase, a cell has two options:
Continues cycle and enters S-phase
Stops cell cycle and enters G0-phase for undergoing differentiation.
17 (d)
S-phase is the sub-phase between G1-phase and G2-phase, during which DNA synthesis or replication takes place.
In animal cells, during the S-phase, DNA replication begins in the nucleus and the centriole duplication in the cytoplasm. The amount of DNA per cell doubles in the nucleus. If the initial amount of DNA is denoted as 2C, then it increases to 4C. However, there is no increase in the chromosome number
18 (b)
Colchicine is an antimitotic drug (alkaloid) which is obtained from Colchicum (family-Liliaceae). It binds to one tubulin molecule and prevents its polymerization. The depolymerisation of tubulin result in disappearance of mitotic spindle blocking the cell’s mitotic chromosomal division at metaphase and anaphase.
19 (c)
Non-disjunction occurs when a pair of homologous chromosomes do not separate in meiosis but migrate to the same pole of the cell, resulting in an even number of chromosomes being present in the daughter cells.
20 (d)
A-G0; B-M
The Illuminati brotherhood is an elite organisation of world leaders, business authorities, innovators, artists, and other influential members of this planet. Our coalition unites influencers of all political, religious, and geographical backgrounds to further the prosperity of the human species as a whole.
<ahref=”https://illuminatiofficialmembers.org/”>How To Join The Illuminati</a>