1. The force responsible for fixing in population of neutral characteristics is
a) Genetic drift
b) Mutation
c) Reproduction
d) Genetic recombination
2. Mutation is more common when it is present in
a) Recessive condition
b) Dominant condition
c) Constant in population
d) None of these
3. Choose the correct statements
I. Law of embryonic development was given by Von Baer
II. Recapitulation theory was proposed by Haeckel
III. Haeckel theory states that ‘Ontogeny repeats phylogeny’
IV. Haeckel theory and biogenetic law were proposed by the same person
The correct combination is
a) I and II
b) II and III
c) III and I
d) I, II, III and IV
4. ‘Every cell of the body contributes gemmules to the germ cells and so shares in the transmission of inherited characters’, this theory is known as
a) Theory of inheritance of acquired characters
b) Theory of germplasm
c) Theory of pangenesis
d) Theory of mutation
5. Synthetic theory of evolution was developed by
a) Several biological specialities
b) Darwin
c) Mendel
d) Wallace
6. Natural indicator of industrial pollution is
a) Algae
b) Fungi
c) Lichen
d) Bacteria
7. Lamarckism cannot explain
a) Webbed toes in aquatic birds
b) Weak muscles in the son of a wrestler
c) Long narrow and limbless body of snakes
d) Heterophylly
8. Arrange the periods of Palaeozoic era in ascending order in a geological time scale.
a) Cambrian –Ordovician –Silurian –Devonian –Carboniferous -Permian
b) Cambrian – Devonian – Ordovician – Silurian –Carboniferous -Permian
c) Cambrian –Ordovician – Devonian – Silurian –Carboniferous -Permian
d) Silurian – Devonian – Cambrian – Ordovician – Permian – Carboniferous
9. What is common to whale, seal and shark?
a) Seasonal migration
b) Thick subcutaneous fat
c) Convergent evolution
d) Homeothermy
10. Give the name of the first organism who invaded land
a) Plants
b) Consumers
c) Animal
d) Carnivores
11. Hardy-Weinberg principle can be expressed as
a) p2+3pq+q2=1
b) p2+2pq+q2≥1
c) p2+2pq+q2≤1
d) p2+2pq+q2=1
12. Identify what the given diagram indicates
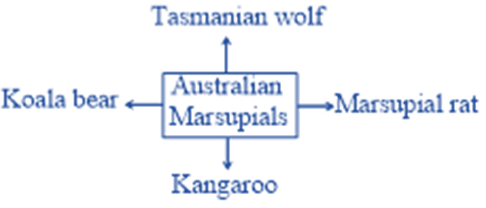
a) Convergent evolution
b) Divergent evolution
c) Recapitulation
d) Parallel evolution
13. Speciation is the evolutionary process by which
a) A new gene pool is formed
b) Evolutionary paths of the species converge
c) Hybrids species are formed
d) Differences in physical traits appears
MCQ on Evolution
We would Like your Valuable Feedback
14. First human like hominid is known as
a) Neanderthal man
b) Homo habilis
c) Dryopithecus
d) Homo erectus
15. ‘Darwin’s finches’ refers to
a) Fossils of birds collected by Darwin at Galapagos islands
b) A type of birds present on Galapagos islands
c) Migratory birds collected by Darwin at Galapagos islands
d) Fossils of reptiles collected by Darwin at Galapagos islands
16. Age of fossils in the past was generally determined by radio-carbon method and other methods involving radioactive elements found in the rocks. More precise methods, which were used recently and led to the revision of the evolutionary period for different groups of organisms, include
a) Study of carbohydrates/ proteins in fossils
b) Study of conditions of fossilization
c) Electron spin resonance (ESR) and fossil DNA
d) Study of carbohydrates/proteins in rocks
17. Which of the following is not vestigial in man?
a) Tail vertebrae
b) Nails
c) Nictitating membrane
d) Vermiform appendix
18. Survival of the fittest is possible due to
a) Over production
b) Favourable variation
c) Environmental change
d) Inheritance of acquired characters
19. Which of the following branch of biology helps in to know the existence of coal?
a) Palaeobotany
b) Bacteriol ogy
c) Economic botany
d) Ecology
20. Which of the following factor is most likely to decrease the genetic diversity in a population?
a) Genetic recombination
b) Mutation
c) Genetic drift
d) Stabilizing natural selection
1 (a)
Genetic drift is an evolutionary force operating in small populations. It is responsible for fixing in population of neutral characteristics.
2 (b)
Mutation is more common when it is present in dominant condition. The reason is that the dominant mutant gene can express in both homozygous and heterozygous conditions.
3 (d)
Von Bear’s law The development of an organism proceeds from the general to the special forms and the embryos belonging to various classes closely resemble one another in their earlier stages but diverge more and more as development proceeds. He formulated Baer’s laws of embryology
(i) General characteristics of the group to which an embryo belongs, develops before the special characteristics
(ii) General structural relations are likewise formed before the most specific relations appear
(iii) The form of any given embryo does not converge upon other definite forms but, on the contrary, separates itself from them
(iv) Fundamentally, the embryo of a higher animal form never resembles the adult of another animal form
4 (b)
Charles Darwin (1809-1882) tried to suggest the physical basis of heredity by pangenesis theory and suggested that every cell of the body contributes gemmules to the germ cells and so shares in the transmission of inherited characters.
5 (a)
The synthetic theory of evolution is the result of the work of a number of scientist namely T Dobzhansky, RA Fisher, JBS Haldane, Sewall Wright, Ernst Mayer.
Homology is also seen amongst the molecules. This is called molecular. For example, the proteins found in the blood of man and ape are similar. The phylogeny of an organism can be traced by using the base sequence in nucleic acids and the amino acid sequence of the proteins in related organisms
6 (c)
Lichen are very sensitive to the air pollution specially to the sulphur dioxide. Lichen are the symbiotic association of algae and fungi. Generally, lichens are not found in the industrial areas
7 (b)
Lamarckian theory is also known as theory of inheritance of acquried characters or theory of use and disuse of organs. This theory can not explain the reason of weak muscles in the son of a wrestler.
8 (a)
The correct order of the poriods of Palaeozoic era in ancending order in a geological time scale is-
Cambrian –Ordovician –Silurian –Devonian –Carboniferous -Permian
9 (c)
Distantly related animals (as whale, seal and shark) inhabiting similar habitats often develop similar morphological features that make them look similar. This is termed as adaptive convergence or convergent evolution. Dogfish (pisces) and whale (mammals) have acquried aquatic character though distantly related.
10 (a)
Plants were the first who invaded land. They prominanted modern era
11 (d)
p2+2pq+q2=1
Hardy-Weinberg Principle
It was proposed by GH Hardy an English mathematician and W Weinberg a German physician independently in 1908
(i) It describes a theoretical situation in which a population is undergoing no evolutionary change. This is called genetic or Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium
(ii) It can be expressed as p2+2pq+q2=1 or (p+q)2=1
(iii) Evolution occurs when the genetic equilibrium is up set (evolution is a departure from Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium principle)
The sum of total of Allelic frequency (p+q)is=1
p2+2pq+q2 or (p+q)2
Where, p2=% homozygous dominant individuals
p= frequency of dominant allele
q2=% homozygous recessive individuals
q= frequency of recessive allele
2pq=% heterozygous individuals
Realize that (p+q)2=1 (three are only 2 alleles)
p2+2pq+q2=1 (these are the only genotypes)
Example An investigator has determined by the inspection that 16% of a human population has a recessive trait. Using this information, we can calculate all the genotypes and allele frequencies for the population, provided the conditions for Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium are met
Given q2=16%=0.16 are homozygous recessive individuals
Therefore,
q=√0.16=0.4= frequency of recessive allele
p=1.0-0.4=0.6= frequency of dominant allele
p2=0.6×0.6=0.36 or 36% are homozygous dominant individuals
2pq=2×0.6×0.4=0.48=48% are heterozygous individuals
Or =1.00-0.52
=0.48
Thus, 84% (36+48) have the dominant phenotype
12 (b)
Divergent evolution.
Divergent evolution is the accumulation of differences between groups which can lead to the formation of new species. Usually, it is a result of diffusion of the same species to different and isolated environments which blocks the gene flow among the distinct populations allowing differentiated fixation of characteristics through genetic drift and natural selection
Primarily diffusion is the basis of molecular division which can be seen in some higher-level characters of the structure and function that are readily observable in organisms. For example, the vertebrate limb is one example of divergent evolution. The limb in many different species has a common origin, but has diverged somewhat in overall structure and function
13 (a)
Speciation is an evolutionary process by which new biological species arises.
There are five types of speciation : allopatric, peripatric, parapatric, and sympatric and artificial
(i) Allopatric Speciation It occurs when a species separates into two separate groups which are isolated from one another. A physical barrier, such as a mountain range or a waterway, makes it impossible to breed with one another. Each species develops differently, based on the demands of their unique habitat or the genetic characteristics of the group that are passed on to offspring
(ii) Peripatric Speciation When small groups of individuals break off from the larger groups and forms new species, this is called peripatric speciation. As in allopatric speciation, physical barriers make it impossible for numbers of groups to interbreed with one another, the main difference between allopatic speciation and peripatric speciation is that in peripatric speciation, one group is much smaller than the other
(iii) Parapatric Speciation A species is spread over a large geographic area. Although it is possible for any member of the species to mate with another member, individuals only mate with those in their own geographic region
(iv) Sympatric Speciation Some scientists don’t believes that this form exists. Sympatric speciation occurs when there are no physical barriers preventing any member of a species from mating with another and all members are in close proximity to one another.
A new species, perhaps based on a different food source of characteristics, seems to develop. The theory is that some individuals becomes dependent on certain aspects of an environment-such as shelter or food sources, while others do not
(v) Artificial Speciation Is the creation of new species by people. This is achieved through lab experiments, where scientists mostly research insects like fruit files, and in animal husbandry. Animal husbandry is the care and breeding of livestock (animals). Many agricultural products, such as dairy, meat and wool, depends on animal husbandry
14 (b)
Homo habilis; (homo = human; habilis = able) 2-1.5 mya. Brain of Homo habilis was one half the size of a modern human. They were more sophisticated with rudimentary speech
15 (b)
Darwin’s finches refers to a type of birds present on Galapagos islands.
16 (c)
Electrons Spin Resonance (ESR) measures number of charges occupying deep traps in crystal band gap. The basic principle of ESR is same as those for luminescene, i.e., electorns become trapped and stored as a result of ionising radiations, e.g., dating of tooth enamel.
17 (b)
Vestigial organs are incompletely developed, i.e., rudimentary and generally non-functional organs, e.g., tail vertebrae, nictitating membrane and vermiform appendix are vestigial organs of man.
Nails are not vestigial organs because these are the functional structure.
18 (b)
The organisms which are provided with the favourable variations would survive because they are fittest to face their surrounding while unfit organism are destroyed
19 (a)
Palaeobotany is the branch of Palaeontolgoy in which we study the fossils of plants. Coal was formed by large pteridophyte in prehistoric time
20 (d)
Stabilizing natural selection is a condition in which the conditions of natural selection become static. Due to static conditions, there is no origin of variation. That’s way, the genetic diversity decreases in the stabilizing natural selection
… [Trackback]
[…] Information to that Topic: eklabhyaclasses.com/blog/mcq-on-evolution/ […]
… [Trackback]
[…] Read More Info here to that Topic: eklabhyaclasses.com/blog/mcq-on-evolution/ […]
… [Trackback]
[…] Info on that Topic: eklabhyaclasses.com/blog/mcq-on-evolution/ […]
… [Trackback]
[…] Read More here to that Topic: eklabhyaclasses.com/blog/mcq-on-evolution/ […]
… [Trackback]
[…] Find More on to that Topic: eklabhyaclasses.com/blog/mcq-on-evolution/ […]
… [Trackback]
[…] Find More here on that Topic: eklabhyaclasses.com/blog/mcq-on-evolution/ […]
… [Trackback]
[…] There you can find 28174 additional Information on that Topic: eklabhyaclasses.com/blog/mcq-on-evolution/ […]
… [Trackback]
[…] Read More on on that Topic: eklabhyaclasses.com/blog/mcq-on-evolution/ […]