M,1. Which of the following are not characteristic features of Fabaceae?
a) Tap root system, compound leaves and receme inflorescence
b) Flowers actinomorphic, twisted aestivation and gamopetalous
c) Stamens ten, introrse, basifixed and dithecous
d) Monocarpellary, ovary superior and bent stigma
2. When the floral appendages are in multiple of 3, 4, 5, they are respectively called
a) Trimerous, tetramerous, pentamerous
b) Penatmerous, tetramerous, trimerous
c) Tripinnate, tetrapinnate, pentapinnate
d) Tetrapinnate, tripnnate, pentapinnate
3. The type of leaf in Daucus carota is
a) Simple
b) Bipinnate
c) Tripinnate
d) Decompound
4. Most advanced fruit is
a) Cypsela
b) Caryopsis
c) Pome
d) Etaerio of drupe
5. Identify A,B and C in the given diagram
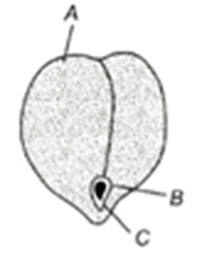
a) A-Seed coat, B-Micropyle, C-Hilum
b) A-Seed coat, B-Hilum, C-Micropyle
c)A-Hilum, B-Seed coat, C-Micropyle
d) A-Micropyle, B-Seed coat, C-Hilum
6. Pedicel of flower is called
a) Thalamus
b) Receptacle
c) Both (a) and (b)
d) Either (a) or (b)
7. A tree that has strong erect stem with hollow internodes and solid nodes, is known as
a) Caudex
b) Deliquescent
c) Scape
d) Culm
8. Identify the correct order (root) from base to root apex
I. Mineral absorption zone
II. Soil penetration zone
III. Cell number increasement zone
V. Cell elongation zone
a) II, I, IV, III
b) I, II, III, IV
c) IV, III, II, I
d) III, IV, I, II
9. Study the following statements and choose the correct option.
I.Buds are present in the axil of leaflets of the compound leaf.
II.Pulvinus leaf-base is present in some leguminous plants.
III.In Alstonia, the petioles expand, become green and synthesize food.
IV.Opposite phyllotaxy is seen in guava.
a) II and IV are correct but I and III are wrong
b) I and III are correct but II and IV are wrong
c) I and IV are correct but II and III are wrong
d) II, III and IV are correct but I is wrong
10. The number of stomata present per cm^2 of a leaf is
a) 1000
b) Less than 100
c) One million
d) None of these
11. Which one of the following series includes the orders Ranales, Parietals and Malvales?
a) Bicarpellatae
b) Thalamiflorae
c) Calyciflorae
d) Disciflorae
12. Which pair of the following plants represents the condition of modification of stipules into spines?
a) Euphorbia and Ziziphus
b) Citrus and Euphorbia
c) Ziziphus and Bougainvillea
d) Bougainvillea and Citrus
13. Amla belongs to family
a) Labiatae
b) Fabaceae
c) Solanaceae
d) Euphorbiaceae
14. The leaves are modified into tendrils, hook, pitcher and bladder in the following plants respectively
a) Sweet pea, cat’s nail, Nepenthes, Utricularia
b) Sweet pea, cat’s nail, Utricularia,Nepenthes
c) Nepenthes, cat’s nail, sweet pea, Utricularia
d) Nepenthes, sweet pea, cat’s nail, Utricularia
15. Fruits are formed in
a) Brassica
b) Fern
c) Cycas
d) Funaria
16. Hypanthodium inflorescence is found in
a) Ficus
b) Tulsi
c) Cedrus
d) Calotropis
17. I. Bear leaves and branches
II. Conduction of water and minerals
III. Storage of food
These are the functions of
a) Root
b) Stem
c) Leaves
d) Root cap
18. Tulip belong to family
a) Asteraceae
b) Liliaceae
c) Brassicaceae
d) Malvaceae
19. The floral formula is of belongs to plant
a) Allium cepa
b) Sunflower
c) Cucurbita
d) Brassica
20. Which of the following is not a characteristic feature of Fabaceae?
a) Descendingly imbricate, ten stamens, diadelphous, ovary superior
b) Sepals five, gamosepalous, imbricate aestivation, placentation marginal
c) Monocarpellary, ovary superior, style long, slightly bent at the apex
d) Corolla, five petals, polypetalous, anterior one large and outermost
1 (b)
In Fabaceae, flowers are zygomorphic, imbricate aestivation, and polypetalous.
2 (a)
A flower may be trimerous, tetramerous or pentamerous when the floral appendages are in multiples of 3, 4 or 5 respectively. Flowers with bracts, reduced leaf found at the base of the pedicel, are called bracteates and those without bracts are called ebracteate
3 (d)
Daucus carota contains decompounds type of leaves, in which leaf rachis divided more than three times and gives rise to small axis on which leaflets are arranged.
4 (d)
According to Hutchinson’s general principles adopted for classification of flowering plants, aggregate fruits (etaerio of drupe) are more recent than single fruits.
5 (b)
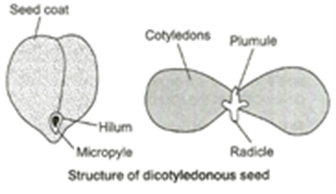
Seed coat The seed is covered by two coverings (layers). The outer layer is thick and tough called testa. The inner one is thin and whitish called tegmen.
Hilum The concave side of seed is darker with a whitish elongated oval scar called hilum.
Micropyle It is the small pore present at the end of hilum. It takes part in absorbing the water during seed germination.
Cotyledons They are also called seed leaves. The two cotyledons are attached to embryo axis in between the plumule and radicle. Cotyledons are large, white, kidney-shaped. They store food
6 (d)
Thalamus or receptacle.
The flower is a reproductive unit in the angiosperms. It is meant for sexual reproduction. A typical flower has four different kinds of whorls arranged successively on the swollen end of the stalk or pedicel called thalamus or receptacle
7 (d)
A stem with hollow internodes and solid nodes is called culm e.g., bamboo, sugarcane, etc.
8 (a)
Below the root cap the area of new cell formation is called meristematic zone. Behind meristematic zone is the area of cell enlargement. Below this zone, the absorption of water and then mineral takes place. This water and mineral absorption comes under the zone of maturation
9 (a)
In some legumes the leaf base may become swollen, which is called the pulvinions.
In opposite phyllotaxy, a pair of leaves arises at each mode and lie opposite to each other as in Calotropic (akon/madar) and guava (Psidium) plants.
10 (a)
The number of stomata present per cm^2 of a leaf is known as stomatal frequency. Normally, it ranges from 1000-60000 per cm^2 or 10-600 mm^2 in different plant species.
11 (b)
Thalamiflorae is a series that contains orders Ranales, Parietales, Malvales, etc.
12 (a)
In Euphorbia of family-Euphorbiaceae and Ziziphus of family-Rhamnaceae, the stipules are modified into spines.
13 (d)
Emblica officinalis is the botanical name of amla and it belongs to family-Euphorbiaceae.
14 (a)
Leaf tendrils Modified thread/spring-like sensitive structures of leaf or leaf parts, e.g., in sweet pea (Lathyrus odortus).
Leaflet hooks In unguis-cati (cat’s nail), the terminal leaflet are modified into cured hooks (as of cat) for climbing.
Pitcher Lamina in Nepenthes is modified into pitcher, which functions in catching and digesting microorganisms or storing water.
Bladder In Utricularia (an aquatic insectivore), a few leaf segments are modified into bladder (balloon-like structures) for trapping small aquatic organisms.
15 (a)
Fruit is the mature ripened ovary of the flower, enclosing the seeds. It is the characteristic feature of Angiospermic plants, e.g., Brassica.
16 (a)
Ficus has hypanthodium inflorescence.
17 (b)
Characteristics of stem
(i) Stem develops from plumule of embryo
(ii) Stem is ascending part of the plant axis
(iii) It bears terminal bud growth
(iv) The stem differentiated into nodes and internodes
(v) The young stem is capable of performing photosynthesis
(vi) Stem are usually positively phototropic, negatively geotropic and negatively hydrotropic
18 (b)
Tulipa, Allium,Lilium, Aloe, Dracaena, etc, belong to family-Liliaceae.
19 (a)
Allium cepa (onion) belongs to family-Amaryllidaceae. The floral formula of Allium cepa is
20 (d)
The corolla of Fabaceae family has five petals, polypetalous, Papilionaceous, descending imbricate aestivation, one posterior long standard, two lateral short wings, two anterior petals joined to each other forming keel.