1. A condition characterized by not having an exact number of chromosomes in a multiple of haploid set is called
a) Polyploidy
b) Synploidy
c) aneuploidy
d) None of these
2. Choose correct option for A,B,C and D
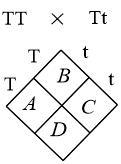
a) A-tt, B-TT, C-TT, D-TT
b) A-Tt, B-Tt, C-Tt, D-Tt
c) A-TT, B-TT, C-Tt, D-TT
d) A-Tt, B-Tt, C-Tt, D-T
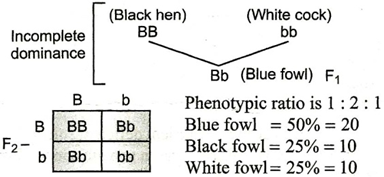
3. When a cross is conducted between black feathered hen and a white feathered cock, blue feathered fowls are formed. When these fowls are allowed for interbreeding, in F2– generation, there are 20 blue fowls. What would be the number of black and white fowls?
a) Black 20, white 10
b) Black 20, white 20
c) Black 10, white 10
d) Black 10, white 20
4. Chromosomes are made up of
a) DNA are protein
b) RNA and DNA
c) DNA and histone
d) Only histones
5. In pedigree analysis, the square, blackened and horizontal lines represents
a) Female, healthy individual, parents
b) Female, affected individual, parents
c) Male, affected individual, parents
d) Male, affected individual, progeny
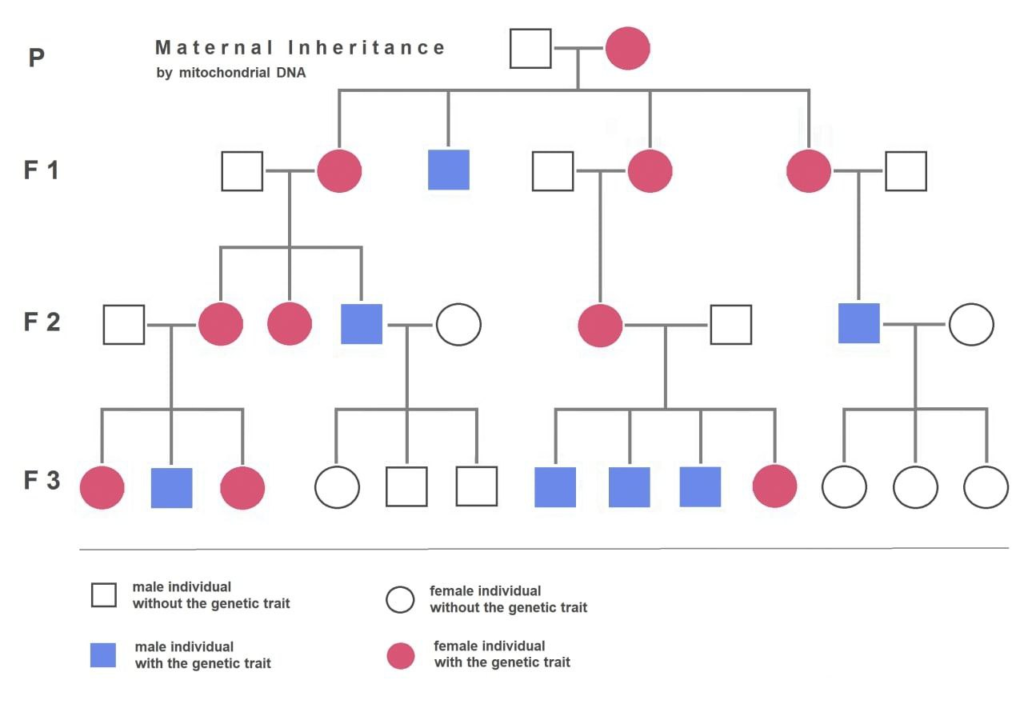
6. Following pedigree chart shows
a) Character is carried by Y-chromosome
b) Character is sex-linked recessive
c) Character is sex-linked dominant
d) Character is recessive autosomal
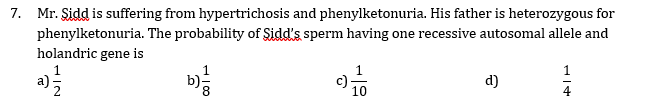
8. F3-generation is obtained by
a) Selfing of F1
b) Selfing of F2
c) Crossing of F1 and F2
d) None of these
9. In which one of the following, complementary gene interaction rato of 9 :7 is observed?
a) Fruit shape in Shepherd’s purse
b) Coat colour in mouse
c) Feather colour in fowl
d) Flower colour in pea
MCQ on Principles of Inheritance
We would Like your Valuable Feedback
10. Starch synthesis gene in pea plant is the example of
a) Single gene produce more than one effects
b) Multiple genes produce more than one effects
c) Two genes produce more than one effects
d) Multiple genes produce less than one effects
11. In Drosophila, the sex is determined by
a) The ratio of pairs of X-chromosomes to the pairs of autosomes
b) Whether the egg is fertilized or develops parthenogenetically
c) The ratio of number of X-chromosomes to the set of autosomes
d) X and Y-chromosomes
12. The 1 : 2 : 1 ratio with the pink flower in the F2-generation indicate the phenomenon of
a) Dominance
b) Codominance
c) Incomplete dominance
d) Segregation
13. Sexual reproduction leads to
a) Genetic recombination
b) Polyploidy
c) Aneuploidy
d) Euploidy
14. Husband has blood group-A and wife has blood group-B. What is the blood group of children?
a) A
b) B
c) AB
d) A, B, AB and O
15. Study the following figure and find out the most probable position at which the crossing over takes place
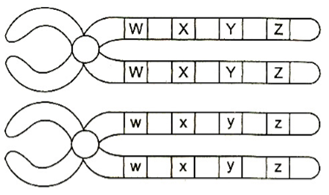
a) w and W
b) X and y
c) y and Z
d) w and z
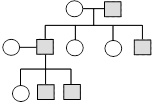
16. Given diagram shows certain type of traits in human. Which one of the following option could be an example of this pattern?
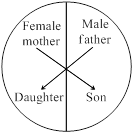
a) Haemophilia
b) Anaemia
c) Phenylketonuria
d) Thalasseamia
17. In case of incomplete dominance, what will be the phenotypic ratio of F2generation?
a) 3 : 1
b) 1 : 2 : 1
c) 1 : 1 : 1 : 1
d) 2 : 2
18. Haemophilia, a X-linked recessive disease is caused due to deficiency of
a) Blood plasma and vitamin–K
b) Blood platelets and haemoglobin
c) Lack of clotting material and vitamin-K
d) All of the above
19. All of this obeys Mendel’s laws except
a) Codominance
b) Independent assortment
c) Dominance
d) Purity of gametes
20. in β-thalassaemia, the affected chromosome is
a) 16th
b) 14th
c) 13th
d) 19th
1 (c)
Aneuploidy is the variations in individual chromosomal number. Actually, loss or gain of individual chromosomes upsets the balance and, hence normal development is not possible.
2 (b)
3 (c)
Black feathered hen = BB
White feathered cock = bb
Blue feathered fowl = Bb
4 (c)
Histones are special type of basic protein associated with DNA and form chromosome. RNA, protein, carbohydrate, fat, doesn’t find in chromosomes
5 (c)
In pedigree
Square represents male blackened square or circle represents affected individual.
Horizontal line represents-parents
The study of inheritance of genetic traits in several generations of a human family in the form of a family tree diagram is called pedigree analysis.
Advantages
(i) It helps in genetic counselling to avoid disorders
(ii) It shows the origin of a trait and flow of a trait in a family
(iii) It is important to know the possibility of a recessive allele that can cause genetic disorders like colour blindness, haemophilia, etc.
Signosed in the pedigree are

6 (a)
In the given pedigree chart only males are affected. So, it can be easily inferred that the given trait is connected to Y-chromosome. The genes, which are present on the Y-chromosome are called holoandric genes
7 (a)
In the gametogenesis meiosis occur. The diploid chromosome become haploid, so the probability of side is sperm lacking one recessive autosomal allele and holandric gene is half
8 (b)
F_3-generation obtained by selfing of F_2-generation.
Mendel cross-pollinated a pure tall pea plant (100-120 cm hight) and a pure dwarf pea plant. (only 22 to 44 cm hight). He called them parental generation, expressed now-a-days by symbol P.
This hybridization popularly called as monohybrid cross
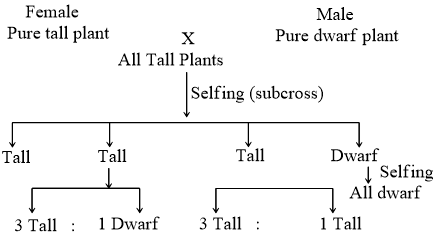
This three generations of pea plants after crossing a pure tall plant with a dwarf one. The plants of F1-generation are all tall, of F2-generation three tall and one dwarf. One third of the tall plants are pure, while the remaining behave as hybrids
F1-generation Seeds collected from the parental generation called first filial generation or F1-generation
F2-generation F1-plants pollinated among them self (self breeding or inbreeding) and seed produced by F1-plants called F2-generation. They were in ratio 3:1 (three tall and one dwarf).
F3-generation Mendel allowed F2-plant to form seed by self-pollination called F3-generation. Mendel observed that tall and dwarf plant behave differently
(i) Dwarf plant produced dwarf plant on self-pollinated
(ii) In tall plants one third plants breed true so they were pure
(iii) Other two third plant behave like parents and give tall to dwarf plants 3 : 1 indicate that their parents have dwarf genes also
9 (d)
W Bateson and R C Punnett observed complementary gene interaction for flower colour in sweet pea (Lathyrus odoratus). In complementary interaction, two separate pairs of genes interact to produce the phenotype in such a way that neither of the dominant genes is expressive unless the other one is present. In F2 generation, complementary genes produce a ratio of 9 : 7.
10 (a)
Occasionally a single gene product may produce more than one effect. For example starch synthesis in pea seeds is controlled by one gene. It has two allele (B and b). Starch is synthesized effectively by BB and have bigger grains. In contrast bb homozygous have lesser efficiency in starch synthesis and produce smaller grains
11 (c)
In Drosophila, sex is determined by the ratio number of X-chromosomes to the set of autosomes.
12 (c)
The genotypic and phenotypic ratio of 1 : 2 : 1 with red, pink and white flowers are produced in Mirabilis jalapa, when red flowered plants (RR) are crossed with white flowered (rr). It occurs due to allelic gene interactions, called, incomplete dominance. In which, both of the allelomorphic genes will have partial or incomplete dominance and F1-hybrid will show mixture of characters of two parents.
13 (a)
Meiosis is an important stage in sexual reproduction. During meiosis, genetic recombination occurs as a result of crossing over.
14 (d)
Blood group of children may be A, B, AB and O.
15 (d)
The genes, which are present very far from each other tend to get unlinked and they arethe most chances for crossing over
16 (a)
Given diagram depicits the sex linked inheritance in given options haemophilia is the sex-linked character
17 (b)
Incomplete dominance or blending inheritance is the phenomenon, in which the two genes of allelomorphic pair are not related as dominant or recessive but each of them expresses itself partially, thus the F1 hybrids exhibit a mixture or blending of characters of both the parents. In F2 generation, the phenotypic ratio obtained is 1 : 2 : 1.
18 (c)
Haemophilia is a disease, which is caused due to lack of blood clotting factor. It appears only in human male which can be transferred to their grandson through his carrier daughter.
19 (a)
In the given option only codominance does not obey Mendel’s laws.
The phenomenon of expression of both the alleles in heterozygote is called codominance. As the result the phenotype is different from both homozygous genotype.
20 (d)
11th.
Thalassaemia
(i) It is an autosome-linked recessive disesase
(ii) It occurs due to either mutation or deletion resulting in reduced rate of synthesis of one of globin chains of haemoglobin
(iii) Anaemia is the characteristic of this disease
(iv) Thalassaemia is classified into two types
α-thalassaemia Production of α-globin chain is affected. It is controlled by the closely linked genes HBA1 and HBA2 on chromosome 16. It occurs due to mutation or deletion of one or more of the four genes.
β-thalassaemia Production of β-globin chain is affected. It occurs due to mutation of one or both HBB genes on chromosome 11

5 thoughts on “MCQ on Principles Of Inheritance & Variation”