1. A complete set of the mouth part of cockroach consists of
a) Labrum and labium
b) Labium, labrum and tongue
c)Larum, mandibles, maxillae and labium
d) Labrum, maxillae and labium
2. In which of the following muscle fibres intercalated disc occurs?
a) In non-striped muscles
b) Between cardiac muscle fibres
c) At the junction of muscle and nerve cells
d) In striped muscles
3. Which of the following part of cockroach’s alimentary canal secretes digestive juices?
a) Malphigian tubule
b) Proventriculus
c) Caecae
d) Crop
4. Consider the following statements related to Rana tigrina and select the correct option stating which are true and which are false
I. Hindlimbs are larger and muscular than forelimbs
II. The alimentary canal of frog is short
III. They respire on the land through skin only
IV. They contains two-chambered heart
I II III IV
a) T F T F
b) F F T T
c) F T T F
d) T T F F
5. During inflammation, which of the following is secreted by connective tissue?
a) Heparin
b) Histamine
c) Serotonin
d) Glucagon
6. Given below the functions of different parts of the alimentary canal of cockroach. Correlate these functions with their respective organs
I. Grinding of food particles
II. Secretion of digestive juices
III. Clearing of haemolymph
The correct set of organs is
a) I. Malpighian tubule
II. Proventericulus
III. Hepatic caecae
b) I. Proventriculus
II. Gastric caecae
III. Malpighian tubule
c) I. Gastric caecae
II. Gizzard
III. Malpighian tubule
d) I. Gizzard
II. Crop
III. Malpighian tubule
7. The compound eyes of cockroaches consists of about
a) 200 hexagonal ommatidia
b) 2000 hexagonal ommatidia
c) 20 hexagonal ommatidia
d) 20,000 hexagonal ommatidia
8. In frog, for the digestion of food, wall of the stomach secretes
a) Pepsins and renin
b) Amylase and tryptophanase
c) HCl and gastric juices
d) HCl and pepsin
MCQ on Anatomy of Structural Organization in Animals
We would Like your Valuable Feedback
9. The major constituent of connective tissue is
a) Vitamin
b) Carbohydrate
c) Lipid
d) Collagen
10. The body of earthworm is divided into
a) 100-120 metamers
b) 150-200 metamers
c) 250-300 metamers
d) 300-350 metamers
11. Which of the following gland is present in man but not in frog?
a) Thyroid gland
b) Salivary gland
c) Pancreas
d) Liver
12. Endothelium of blood vessels is made up of
a) Simple cuboidal epithelium
b) Simple squamous epithelium
c) Simple columnar epithelium
d) Simple non-ciliated columnar epithelium
13. Ciliated epithelium is present in
a) Trachea
b) Ureter
c) intestine
d) Nasal chamber
14. In water, the skin of the frog performs the function of
a) Osmosis
b) Plasmolysis
c) Diffusion
d) Thermoregulation
15. Which type of tissue is present in human heart?
a) Epithelial tissue
b) Muscular tissue and neural tissue
c) Connective tissue
d) All of the above
16. Given below the diagram of the ventral view of earthworm’s body. Identify A to F and choose the correct combination of options
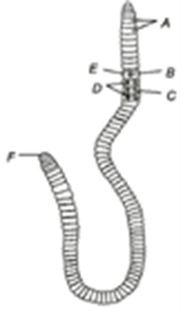
a) A-Setae, B-Female genital aperture, C-Male genital aperture, D-Genital papillae, E-Clitellum, F-Anus
b) A- Anus, B- Setae, C-Male genital aperture, D- Female genital aperture, E-Genital papillae, F- Clitellum
c) A-Setae, B- Male genital aperture, C- Female genital aperture, D-Genital papillae, E-Clitellum, F-Anus
d) A-Nephridiopores, B- Setae, C-Nuclei, D-Metamers, E-Prostomium, F-Anus
17. Identify A, B and C in given figures and choose the correct combination of options
a) A-Unicellular gland, B-Multicellular gland, C-Multilayered cells
b) A-Multicellular gland, B-Unicellular gland, C-Squamous epithelium
c) A-Goblet gland, B-Multicellular gland, C-Columnar epithelium
d) A-Flattened cell, B-Multilayered cells, C-Transitional epithelium
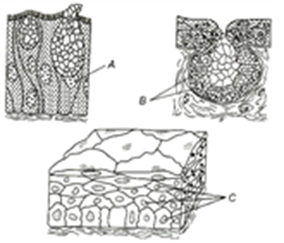
18. Consider the following statement about frog’s digestive system
I. Food is captured by the bilobed tongue
II. Partially digested food is called chyme. It is passed from the stomach to the first part of intestine
III. Bile digests carbohydrates and proteins
IV. Inner wall of the intestine contains cilia
Which of the above given statement are incorrect?
a) I and II
b) II and III
c) III and IV
d) I and IV
19. The cell junctions called tight, adhering and gap junctions are found in
a) Muscular tissue
b) Connective tissue
c) Epithelial tissue
d) Neural tissue
20. The principal role of setae in earthworm is
a) Respiration
b) Excretion
c) Locomotion
d) Assimilation

… [Trackback]
[…] There you can find 96687 more Info on that Topic: eklabhyaclasses.com/blog/mcq-on-structural-organization-in-animals-2/ […]
… [Trackback]
[…] Read More to that Topic: eklabhyaclasses.com/blog/mcq-on-structural-organization-in-animals-2/ […]
… [Trackback]
[…] Here you can find 29556 more Information on that Topic: eklabhyaclasses.com/blog/mcq-on-structural-organization-in-animals-2/ […]