1. According to binomial nomenclature, scientific name of an organism consists of
a) Generic name
b) Specific epithet
c) Both (a) and (b)
d) None of these
2. Different (various) group of ranks or levels in classification is known/called as
a) Category
b) Order
c) Genera
d) Taxon
3. Species is considered as
a) Largest taxon of taxonomy/classification
b) Key of taxonomy/classification
c) Smallest taxon of faxonomy/classification
d) Both small and largest unit of taxonomy/classification
4. Which one of the following is the feature of phylum-Chordata is also exhibited by adult tunicate?
a) Possession of visceral slits
b) Possession of a ventral chord
c) Possession of closed vascular system
d) Possession of ventral tubular nervous system
5. Choose the correct classification for the given plant
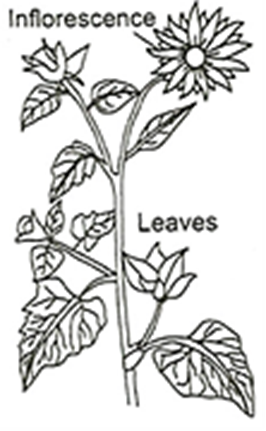
a) Plantae, Anglosperm, Monocotyledons
b) Plantae, Anglosperm, Dicotyledons
c) Plantae, Gymnosperm, Monocot
d) Plantae, Pteridophytes, Dicot
6. Scientific study of diversity of organisms and their evolutionary relationship is
a) Morphology
b) Anatomy
c) Taxonomy
d) Systematics
7. Different (various) group of ranks or levels in classification is known/called as
a) Category
b) Order
c) Genera
d) Taxon
8.The concept that monocots are more primitive than dicots was proposed by
a) Bentham and Hooker
b) Theophrastus
c) Aristole
d) Engler and Prantl
9. A defining property or characteristic of living organisms is
a) Increase in mass
b) Development
c) Response to external stimuli
d) Growth
10. What is the old name of Indian Board of wildlife
a) National Board of Wildlife Animal
b) Central Board of Wildlife
c) Board of Wildlife
d) Wildlife Protection Board
11. Species are consider as
a) Artificial concept of human mind which cannot be defined in absolute terms
b) Real units of classification devised by taxonomists
c) Real basic units of classification
d) The lowest units of classification
12. In plants growth occur by … throughout their life span.
Choose an appropriate option to complete the given NCERT statement
a) Cell dedifferentiation
b) Cell differentiation
c) Cell multiplication
d) None of these
13. Growth in unicellular organisms can be observed by
a) Counting the mass of cultured cells
b) Analysing the amount of nutrient absorb by living organism
c) Growth can not be observed
d) In vitro culture by simply counting the number of cells under microscope
14. Largest herbarium in the world is
a) Conservatory and Botanical Garden, Geneva
b) New York Botanical Garden
c) Royal Botanical Garden, Kew (London)
d) British, Museum of Natural History
15. Taxonomic hierarchy refers to
a) Stepwise arrangement of all categories for classification of plants and animals
b) A group of senior taxonomists, who decide the nomenclature of plants and animals
c) A list of botanists or zoologists, who have worked on taxonomy of a species or group
d) Classification of a species based on fossil record
16. A perennial shrub has compound leaves and solitary zygomorphic and epigynous flowers. Each flower reveals dichlamydeous condition with many stamens and multiple fruit with exalbuminous seeds. What is the ratio of advanced and primitive characters in it?
a) 1:2
b) 2:3
c) 1:1
d) 3:2
17. A germplasm is a
a) Collection of seeds or plants consists diverse alleles of all genes in a crop
b) Collection of specimens of all the species of botanical garden
c) Collection of hybrid varieties of plants
d) Seed or pollar collection of threatened species of a group
18. Which one of the following has a real existence?
a) Genus
b) Species
c) Family
d) Order
19. Binomial system of classification was based on
a) Embryology
b) Morphology
c) Cytology
d) Anatomy
20. Which is not a category?
a) Asteraceae/Fabaceae
b) Species
c) Phylum
d) Class
1 (c)
Binomial nomenclature provide a distinct and proper scientific name to organism, each consisting of two words, first generic name and second specific name, which are derived from Latin language.
Scientific names are printed in italics and hand written name is underlined (zig zag)
2 (d)
→ A taxon is the taxonomic group of any rank in the system of classification
3 (c)
Species is basic/lowest/smallest unit of taxonomy. According to Earnst Mayr species are group of interbreeding natural populations. Which are reproductively isolated from other such groups. It contains most similar organisms
4 (a)
Presence of visceral slits is exhibited by both Chordata and adult Tunicata members
5 (b)
The given figure shows flowering plant so, plant belongs to angiosperm. And the leaf venation is reticulate so plant is dicot
6 (d)
The discipline of biology which deals with the kind and diversity of all organisms and the existing relationship amongest them is called systematics. The word ‘systematics’ is derived from Latin word systema which means systematic arrangement of organisms. It was first used by Carolus Linnaeus. He used SystemaNaturae as the title of his publication. The scope of systematics was later enlarged to include identification, nomenclature and classification. Systematic takes into account evolutionary relationships between organisms.
7 (d)
→ A taxon is the taxonomic group of any rank in the system of classification
8 (d)
The concept that monocots are more primitive than dicots was proposed by Engler and Prantl.
9 (c)
All living organism from prokaryotes to the most complex eukaryotes can respond external stimuli. The non-living things do not have this property at all
10 (b)
Present Indian Board of Wildlife is former Central Board of Wildlife is former Central Board of Wildlife. IBWL concerned with conservation of wildlife and run project to save wildlife and public awareness
11 (c)
A species is a group of organisms that interbreed freely in their natural setting and do not interbreed with other population. In simple words, members of one species are reproductively isolated from members of other species. Species is the real basic unit for understanding taxonomy as well as evolution.
12 (c)
In plant growth occurs by cell division or multiplication continuously in all parts throughout their life span
13 (d)
Growth also occur in unicellular organisms by cell division. It can be observed in vitro culture by counting the number of cell under microscope
14 (c)
Largest herbarium in the world is herbarium of Royal Botanical Garden, Kew (London) which contains more than 6,00,000 specimens
15 (a)
Taxonomic hierarchy refers to stepwise arrangement of all categories for classification of plants and animals. The categories in taxonomic hierarchy are: Kingdom → Division (Phylum) → Class → Order → Family → Genus → Species
16 (c)
According to phylogenetic system of classification, primitive charecters are perenniall and shrubby nature, solitary flower, numerous stamens multiple or aggregate fruit, while advanced characters are compound leaves, zygomorphic flowers, epigynous flowers, fused stamens (dichlamydeous condition) and albuminous seeds.
Thus, the ratio of advanced and primitive characters according to question is 1:1.
17 (a)
Germplasm is a collection seeds/plants which consists diverse alleles of all gene in a crop
18 (b)
Species is group of interbreeding populations according to biological concept of species (proposed by Mayr) and new species is formed from existing species
19 (b)
Binomial system of classification was based on morphological characteristic of an organism
20 (a)
Species, phylum and class are all taxonomic categories, while Asteraceae/Fabaceae are families
5 thoughts on “MCQ On The Living World”