1. Arrange the following plants in ascending order based on the number of xylem strands in their roots.
I. Trapa II. Pisum III. Castanea IV. Nicotiana
a) II, IV, III, and I
b) III, IV, II, and I
c) IV, III, I, and II
d) I, IV, II and III
2. ‘Quiescent centre theory’ was proposed by
a) Nagelli
b) Schmidt
c) Hanstein
d) Clowes
3. In an annual ring, the light coloured part is known as
a) Early wood
b) Late wood
c) Heartwood
d) Sapwood
4. In roots the
a) Protoxylem lies towards the periphery
b) Metaxylem lies towards the pith (centre)
c) Both (a) and (b)
d) Endarch condition is found
5. Epidermis is often covered with a waxy thick layer called
a) Cuticle
b) Suberin
c) Supporting cell
d) All of these
6. I. Protection of internal tissue
II. Prevention of entry of any harmful organism
III. Minimising surface transpiration
IV. Protection against excessive heating up
These are the functions of which of the following?
a) Epidermis
b) Cortex
c) Hypodermis
d) Cuticle
7. In a woody dicotyledonous tree, which of the following parts will mainly consist of primary tissues?
a) Stem and root
b) All parts
c) Shoot tips and root tips
d) Flowers, fruits and leaves
8. Old stem on Combretum has
a) Inter and intraxylary phloem
b) Inter and extraxylary phloem
c) Intra and extraxylary phloem
d) All of the above
9. Atactostele type of stele is found in
a) Dicot
b) Monocots
c) Both (a) and (b)
d) Only in gymnosperm
10. I. Sieve tube conduct organic food longitudinally
II. Xylem parenchyma cells stores food and help in lateral conduction of sap
Select the correct option
a) I is incorrect, but II is correct
b) II is incorrect, but I is correct
c) I and II are correct
d) I and II are incorrect
11. Growth rings are formed due to activity of
a) Extrastelar cambium
b) Intrastelar cambium
c) Interstelar cambium
d) Both (b) and (c)
12. Water impermeable, waxy material secreted by endodermal cells is called
a) Lignin
b) Suberin
c) Conjuctive tissue
d) Pectin
13. Tyloses are balloon-like ingrowths in vessels developing from the adjoining
a) Fibres through pits on vessel wall
b) Fibres through the general surface of vessel wall
c) Parenchyma through pits on vessel wall
d) Parenchyma through the general surface of vessel wall
14. Select the correct statement from the following
a) The cells of the permanent tissue do not generally divide
b) Permanent tissues having all cells similar in structure and function are called simple tissues
c) Permanent tissues having many different types of cells are called complex tissues
d) All of the above
15. Tissues involved in secondary growth is/are
I. intercalary stem
II. vascular cambium
III. cork cambium
Select the correct options from below
a) I and II
b) II and III
c) I and III
d) I, II and III
16. Which is a characteristic of dicots?
a) Roots develop from radicle
b) Secondary growth usually absent
c) Floral parts in multiple of three
d) Parallel leaf veins
17. Identify the plant parts whose transverse section shows a clear and prominent pith.
a) Dicot and monocot stems
b) Dicot stem and monocot root
c) Dicot and monocot roots
d) Dicot stem and dicot root
18. A tree grows at the rate of 0.5 m per year. What will be the height of the board fixed at 1.5 m above the base five years ago?
a) 4.0 m
b) 3.5 m
c) 1.5 m
d) 4.5 m
19. Mesophylls of monocotyledon leaf are not differentiated into
a) Palisade tissue
b) Spongy parenchyma
c) Bulliform cells
d) Both (a) and (b)
20. In the given diagram of secondary growth of dicot root, identify A to D and choose the correct option
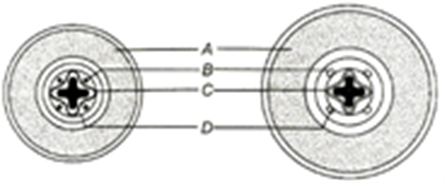
a) A-Cortex, B-Primary phloem, C-Cambial ring, D-Protoxylem
b) A-Cortex, B-Primary phloem, C-Cambial ring, D-Pericycle
c) A-Cortex, B-Primary phloem, C-Primary xylem, D-Pericycle
d) A-Cortex, B-Primary phloem, C-Primary xylem, D-Protoxyleme
1 (d)
Only one xylem strand occurs in the slender root of the hydrophyte Trapa natans. In Nicotiana, the roots are diarch. In Pisum, the root is triarch. In Castanea, the root is tetrarch.
2 (d)
Clowes proposed quiescent centre theory.
3 (a)
Spring wood plus autumn wood of a year constitute annual ring. The spring wood (also called early wood) is light in colour and constitute major part of annual ring. The autumn wood (also called late wood) is darker in colour.
Wood consists of secondary xylem. The central hard, tough and darker region of wood constitutes heart wood while peripheral portion constitutes sap wood. But these are not specified in annual rings.
4 (c)
In roots the protoxylem lies towards the periphery and metaxylem lies toward the centre. Such arrangement is called exarch
5 (a)
The outside of the epidermis is often covered with waxy thick layer called cuticle, which prevents the loss of water. Cuticle is absent in roots
6 (a)
The various function of the epidermis are
(i) Protection of internal tissues
(ii) Prevention of entry of harmful organisms
(iii) Minimising surface transpiration by having thick cuticle
(iv) Exchange of gases through stomata
(v) Protection against excessive heating up and sudden changes in temperature with the help of hair (as in sunflower)
7 (c)
In a woody dicotyledonous tree, shoot tips and root tips consist of primary tissues.
8 (b)
In Combretum and Entada, the cambium shows abnormal behavior by cutting phloem on the inner as well as at certain places for a short period and then resumes normal activity.
9 (b)
Monocots have atactostele, in which vascular bundles are arranged into more than one ring and they are usually found at the centre of the stem
10 (c)
Phloem lie towards the pericyclet on the outerside of vascular bundle. Phloem consists of sieve tubes, companion cells, phloem parenchyma and phloem fibres. The companion cells and phloem parenchyma are connected with sieve tubes through pits. They help in lateral flow of organic food. The companion cells also control the functions of the sieve tubes. The sieve tubes conduct organic food longitudinally
11 (d)
Intrastelar cambium is the cambium present between xylem and phloem (i.e., within the stele), and the interstelar cambium, is present between steles (vascular bundle) and show growth rings formation.
12 (b)
Suberin.
The innermost layer of cortex is called endodermis. It comprises a single layer of barrel-shaped cells without any intercellular spaces. The tangential as well as radial walls of the endodermal cells have a deposition of water impermeable, waxy material called suberin in the form of casparian strips
13 (c)
Tyloses are protrusions of the axial and ray parenchyma cells, which enter in tracheary elements.
14 (d)
The cell of the permanent tissues do not generally divide further. Permanent tissues having all cells similar in structure and function are called simple tissues. Permanent tissues having different types of cells together are called complex tissues
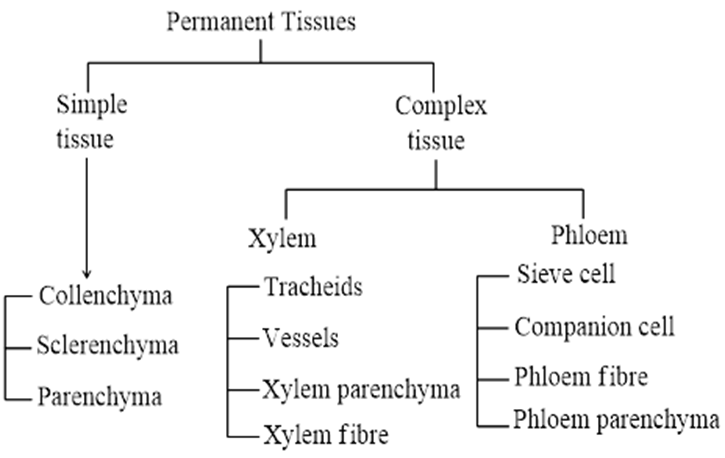
15 (b)
The tissue involved in secondary growth are two lateral meristems
(i) Vascular cambium
(ii) Cork cambium
16 (a)
In dicots, flower parts in four or five or multiple of these. They have leaf veins in the form of a net and secondary growth is present.
17 (b)
A thin-walled pith is generally present in monocot roots, while in dicot roots, a thin-walled conjunctive tissue is present in between vascular elements. Thin-walled pith is also well marked in dicot stems but absent in monocot stems.
18 (c)
The increase in height of a plant is due to apical meristem. Therefore, the height of the board remains same after five years.
19 (d)
In dicotyledon leaves, the mesophyll tissue is differentiated into the palisade tissue and spongy parenchyma but in monocot such differentiation is not seen
20 (d)
6 thoughts on “MCQ on Anatomy Of Flowering Plants ”