MCQ on Body Fluids And Circulation
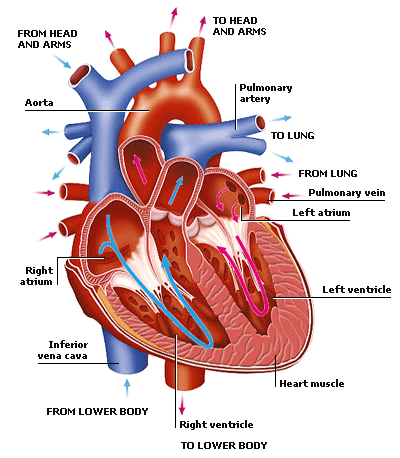
1. Which of the following blood vessels in the circulatory system of frog has more deoxygenated blood?
a) Pulmonary artery
b) Precaval veins
c) Pulmocutaneous artery
d) Pulmocutaneous vein
2. Which one indicates hypertension or high blood pressure (BP)
a) 120/80
b) 110/70
c) 130/80
d) 140/90
3. Identify the correct statement
I. The impulse of the heart beat originates from SAN
II. Rate of the heart is determined by SAN
III. Bundle of His/AV bundle is present in the interventricular septum
IV. Atrio Ventricular Node (AVN) is situated in the lower left corner of the right auricle
Choose the correct option
a) All except II
b) All except I
c) All except III
d) All of these
4. Choose the correct pathway on the transmission of impulse in the heart beat.
a) AV-node → SA-node → Bundle of His → Purkinje fibres
b) SA-node → AV-node → Bundle of His → Purkinje fibres
c) SA-node → Bundle of His → AV-node → Purkinje fibres
d) AV-node → Bundle of His → SA-node → Purkinje fibres
5. Water circulatory system in found in
I. Sponge
II. Hydra
III. Annelida
IV. Starfish
V. Arthropoda
Choose the correct option
a) I, II and III
b) III, IV and V
c) I, II and IV
d) II, IV and V
6. Which of the following is an example of buffer system in blood?
a) Haemoglobin and oxyhaemoglobin
b) Oxygen and carbon dioxide
c) Albumin and globulin
d) Sodium bicarbonate and carbonic acid
7. In an open circulatory system,
a) There is no distinction between the blood and the tissue fluid
b) Of tissue fluid is absent
c) No need of blood vessels
d) Open space or sinuses are absent
8. Primary blood cells are formed in
a) Plasma
b) Bone marrow
c) Liver
d) Spleen
9. Properties of leucocytes are
I. they are nucleated
II. they are denucleated like RBC
III. they are 6000-8000 mm(-3) of blood
IV. they are long lived
V. they are short lived
Choose the appropriate option with correct properties
a) I, III and V
b) II, IV and V
c) I, IV and V
d) I, III and V
MCQ on Body Fluids And Circulation
We would Like your Valuable Feedback
10. SAN can generate impulses
a) 70 – 75 min(-1)
b) 50 – 55 min(-1)
c) 100 – 150 min(-1)
d) 35– 40 min(-1)
11. Haematuria means
a) RBCs in the urine
b) WBCs in the urine
c) Both (a) and (b)
d) None of these
12. An oval depression called fossa ovalis, is seen on
a) Inter-atrial septum
b) Inter-ventricular septum
c) Right-auriculo-ventricular septum
d) Left auriculo-ventricular septum
13. Which of the following acts as ‘middle man of the body’?
a) Plasma
b) Lymph
c) RBCs
d) RBCs
14. coronary heart disease is due to
a) Streptococci bacteria
b) Inflammation of pericardium
c) Weakening of the heart valves
d) Insufficient blood supply to the heart muscles
15. Pulse beat is measured from
a) Arteries
b) Veins
c) Capillaries
d) Nerves
16. Which of the following is incorrect?
a) Heart is endodermal in origin
b) Human heart is situated in the between the two lungs slightly tilted to left
c) Heart is a double walled membranous bag
d) Human heart has two atria and two ventricles
17. Lymphatic system is an elaborated network of vessels which collect the
a) Interstitial fluid
b) Intrastitial fluid
c) Plasma fluid
d) Protein fluid
18. In human heart, identify the correct statements a
I. Volume of both the atria is the greater than the volume and both ventricles
II. Volume of both the ventricle is greater than the volume of both the atria
III. Inter-ventricular septum separates the right and the left atria
IV. Atrio ventricular septum don’t separates the atrium and ventricle
Choose the correct option accordingly
a) All except I
b) All except II
c) All except III
d) All except IV
19. SAN generates an action potential which stimulates both the …A… to undergo a simultaneous contraction called …B… . This increases the flow of the blood into the ventricles by about …C… percentage
Choose the correct option for A, B and C
a) A-atria, B-asterial systole, C-30
b) A-ventricle, B-asterial systole, C-30
c) A-atria, B-ventricular diastole, C-30
d) A-atria, B-asterial diastole, C-30
20. The normal percentage of glucose in the blood of man is 0.1%. it is found in
a) Plasma
b) RBCs
c) WBCs
d) Serum
1 (a)
In frog, pulmonary artery is a paired artery that carry more deoxygenated blood from the right ventricle of the heart to the lungs.
2 (d)
If repeated checks of blood pressure of an individual is 140/90 (140 over 90) or higher, it show hypertension. High blood pressure leads to heart diseases and also affects the vital organs like brain and kidney
3 (c)
All except III.
Auto-Rhythmicity of Heart
Automatic rhythmicity of the heart is the ability to contract spontaneously. Mammalian heart is myogenic. It means heart beat results from a wave of electrical potential called cardiac impulse arising from sinoatrial node SA node and spreading over cardiac chambers.
SA-node lies in the wall of right atrium near opening of superior vena cava and contract about 72 times per minute. Form SA node cardiac impulse travels to atrioventricular node (lies between right atrium and ventricle)
Then pass to AV bundle (also called bundle to His) and its branches reaches to the Purkinje fibres in ventricles.
Bundle of His provides the only route for the transmission of wave of excitation from atria to ventricles. Purkinje fibres conducts the impulses five times more rapidly than surrounding cells. It forms a pathway for conduction of impulse that ensures that the heart muscle contracts in the most efficient manner
4 (b)
The correct pathway of the transmission of impulses in the heart beat is
SA-node → AV-node → Bundle of His → Purkinje fibers
5 (c)
Water is the medium of transportation, in sponges (water canal system) Hydra (gastro vascular system) and starfish (ambulacral system)
6 (d)
A buffer is a chemical or combination of chemicals that can both take up and release hydrogen ions. Carbonic acid (H2 CO3) and sodium bicarbonate (NaHCO3) help buffering human blood because H2 CO3 is a weak acid that does not totally dissociate, when excess hydrogen ions are present in blood, the reaction goes to the left and carbonic acid forms to maintain the pH.
H2 CO3 ⇌ H+ + HCO3–
Carbonic acid Hydrogen ion Bicarbonate ion
7 (a)
In open circulatory system instead of capillaries, blood vessels join directly with the open sinuses. Blood is actually a combination of blood and interstitial fluid called haemolymph which is forced from the blood vessels into the large sinuses, where it actually, baths the internal organs
8 (b)
Primary blood cells are formed in bone marrow. The process of formation of blood is called haemopoiesis.
9 (a)
I, III, V.
Leucocytes or white blood corpuscles which are without haemoglobin and therefore, they are colourless and considerably larger than RBC. The normal WBC count is 6000-8000 per cubin mm of blood. Lower count is called leukopenia and high WBC count is termed as leukaemia or leucocytosis. The life span of WBC in man is about 10-30 days
10 (a)
70-75 min(-1).
Auto-Rhythmicity of Heart
Automatic rhythmicity of the heart is the ability to contract spontaneously. Mammalian heart is myogenic. It means heart beat results from a wave of electrical potential called cardiac impulse arising from sinoatrial node SA node and spreading over cardiac chambers.
SA-node lies in the wall of right atrium near opening of superior vena cava and contract about 72 times per minute. Form SA node cardiac impulse travels to atrioventricular node (lies between right atrium and ventricle)
Then pass to AV bundle (also called bundle to His) and its branches reaches to the Purkinje fibers in ventricles.
Bundle of His provides the only route for the transmission of wave of excitation from atria to ventricles. Purkinje fibres conducts the impulses five times more rapidly than surrounding cells. It forms a pathway for conduction of impulse that ensures that the heart muscle contracts in the most efficient manner
11 (a)
Haematuria is the presence of blood cells (RBCs) in urine. The presence of WBCs or pus in the urine is called pyuria.
12 (a)
An oval depression called fossa ovalis is present in the inter auricular septum within the right auricle. This depression is present as an oval foramen in embryo called foramen ovale. Through this foramen, the blood from right auricle is communicated towards left auricle in embryo.
13 (b)
Lymph acts as middle man of the body.
14 (d)
Coronary heart disease occurs due to insufficient blood supply to the heart muscle.
15 (a)
Pulse is rhythmic contraction and relaxation in the aorta and its main arteries. Thus, pulse is a wave of increase, which passes through arteries as the left ventricle pumps its blood into aorta. Pulse is a regular jerk of an artery. Pulse is usually taken on a radial artery in wrist.
16 (a)
Heart is mesodermal in origin
17 (a)
An elaborate network of vessels called the lymphatic system collects the interstitial fluid and drains it back to the major vein. This network is called lymphatic system and the process is called lymphatic circulation
18 (b)
Volume of both atrium is less than the volume of both ventricles.
Interventricular septum separates the right and left ventricles.
Atrioventricular septum separates the atrium and ventricles
19 (a)
A-atria, B-atrial systole, C-30.
Auto-Rhythmicity of Heart
Automatic rhythmicity of the heart is the ability to contract spontaneously. Mammalian heart is myogenic. It means heart beat results from a wave of electrical potential called cardiac impulse arising from sinoatrial node SA node and spreading over cardiac chambers.
SA-node lies in the wall of right atrium near opening of superior vena cava and contract about 72 times per minute. Form SA node cardiac impulse travels to atrioventricular node (lies between right atrium and ventricle)
Then pass to AV bundle (also called bundle to His) and its branches reaches to the Purkinje fibers in ventricles.
Bundle of His provides the only route for the transmission of wave of excitation from atria to ventricles. Purkinje fibres conducts the impulses five times more rapidly than surrounding cells. It forms a pathway for conduction of impulse that ensures that the heart muscle contracts in the most efficient manner
20 (a)
After the digestion of carbohydrates, proteins and fats, the amino acid, glucose, fatty acids, glycerol and vitamins, etc, are absorbed into the blood plasma from the alimentary tract.
5 thoughts on “MCQ on Body Fluids And Circulation ”