MCQ ON THERMAL PROPERTIES OF MATTER MCQ ON THERMAL PROPERTIES OF MATTER
1. In a pressure cooker, cooking is faster because the increase of vapour pressure
a) Increases specific heat
b) Decreases specific heat
c) Decreases the boiling point
d) Increases the boiling point
2. The heat is flowing through a rod of length 50 cm and area of cross-section 5cm2. Its ends are respectively at 25℃ and 125℃. The coefficient of thermal conductivity of the material of the rod is 0.092 kcal/m×s×℃. The temperature gradient in the rod is
a) 2℃/cm
b) 2℃/m
c) 20℃/cm
d) 20℃/m
3. The plots of intensity of radiation versus wavelength of three black bodies at temperatures T1,T2 and T3 are shown. Then,
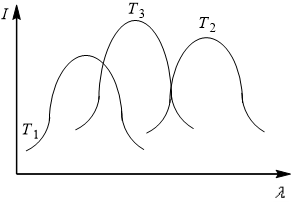
a) T3>T2>T1
b) T1>T2>T3
c) T2>T3>T1
d) T1>T3>T2
4. A composite metal bar of uniform section is made up of length 25 cm of copper, 10 cm of nickel and 15 cm of aluminium. Each part being in perfect thermal contact with the adjoining part. The copper end of the composite rod is maintained at 100℃ and the aluminium end at 0℃. The whole rod is covered with belt so that no heat loss occurs at the sides. If KCu=2KAl and KAl=3KNi, then what will be the temperatures of Cu-Ni and Ni-Al junctions respectively
| Cu | Ni | AI |
a) 23.33℃ and 78.8℃
b) 83.33℃ and 20℃
c) 50℃ and 30℃
d) 30℃ and 50℃
5. Mercury boils at 367°C.However,mercury thermometers are made such that they can measure temperature are made such that they can measure temperature upto 500°C.This is done by
a) Maintaining vacuum above mercury column in the stem of the thermometer
b) Filling nitrogen gas at high pressure above the mercury column
c) Filling oxygen gas at high pressure above the mercury column
d) Filling nitrogen gas at low pressure above the mercury column
6. A student takes 50gm wax (specific heat =0.6 kcal/kg℃) and heats it till it boils. The graph between temperature and time is as follows. Heat supplied to the wax per minute and boiling point are respectively
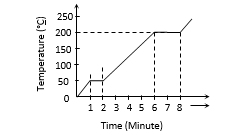
a) 500 cal,50℃
b) 1000 cal,100℃
c) 1500 cal,200℃
d) 1000 cal,200℃
7. Dry ice is
a) Ice cube
b) Sodium chloride
c) Liquid nitrogen
d) Solid carbon dioxide
8. A partition wall has two layers A and B in contanct, each made of a different material. They have the same thickness but the thermal conductivity of layer A is twice that of layer B. If the steady state temperature difference across the wall is 60K, then the corresponding difference across the layer A is
a) 10 K
b) 20 K
c) 30 K
d) 40 K
9. A closed bottle containing water at 30℃ is carried to the moon in a space-ship. If it is placed on the surface of the moon, what will happen to the water as soon as the lid is opened
a) Water will boil
b) Water will freeze
c) Nothing will happen on it
d) It will decompose into H2 and O2
10. The coefficient of thermal conductivity of copper is 9 times that of steel. In the composite cylindrical bar shown in the figure, what will be the temperature at the junction of copper and steel
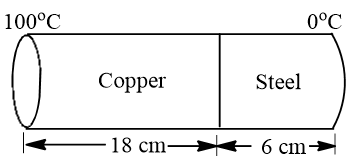
a) 75℃
b) 67℃
c) 25℃
d) 33℃
11. Three discs, A,B and C having radii 2 m, 4 m and 6 m respectively are coated with carbon black on their outer surfaces. The wavelengths corresponding to maximum intensitios are 300 nm, 400 nm and 500 nm respectively. The power radiated by them are QA,QBand QC respectively
a) QA is maximum
b) QB is maximum
c) QC is maximum
d) QA=QB=QC
MCQ on Thermal Properties of Matter
We would Like your Valuable Feedback
12. Two rods of different materials having coefficient of thermal expansions α1 and α2 and Young’s moduli Y1 and Y2 respectively are fixed between two rigid walls. The rods are heated, such that they undergo the same increase in temperature. There is no bending of rods. If α1/α2=2/3 and stresses developed in the two rods are equal, then Y1/Y2 is
a) 3/2
b) 1
c) 2/3
d) 1/2
13. Four identical rods of same material are joined end to end to form a square. If the temperature difference between the ends of a diagonal is 100℃, then the temperature difference between the ends of other diagonal will be
a) 0℃
b) 100/l℃; where l is the length of each rod
c) 100/2l℃
d) 100℃
14. On investigation of light from three different stars A,B and C, it was found that in the spectrum of A the intensity of red colour is maximum, in B the intensity of blue colour is maximum and in C the intensity of yellow colour is maximum. From these observations it can be concluded that
a) The temperatures of A is maximum, B is minimum and C is intermediate
b) The temperatures of A is maximum, C is minimum and B is intermediate
c) The temperatures of B is maximum, A is minimum and C is intermediate
d) The temperatures of C is maximum, B is minimum and A is intermediate
15. In a room where the temperature is 30℃, a body cools form 61℃ to 59℃ in 4 min. The time (in minutes) taken by the body to cool from 51℃ to 49℃ will be
a) 8
b) 5
c) 6
d) 4
16. When red glass is heated in dark room it will seen
a) green
b) Purple
c) Black
d) Yellow
17. Which of the following cylindrical rods will conduct most heat, when their ends are maintained at the same steady temperature
a) Length 1 m; radius 1 cm
b) Length 2 m; radius 1 cm
c) Length 2 m; radius 2 cm
d) Length 1 m; radius 2 cm
18. A sphere, a cube and a thin circular plate, all made of the same material and having the same mass are initially heated to a temperature of 1000℃. Which one of these will cool first
a) Plate
b) Sphere
c) Cube
d) None of these
19. A steel meter scale is to be ruled so that millimeter intervals are accurate within about
5×10(-5) mm at a certain temperature. The maximum temperature variation allowable during the ruling is (Coefficient of linear expansion of steel =10×10(-6) K(-1) )
a) 2℃
b) 5℃
c) 7℃
d) 10℃
20. Colour of shinning bright star is an indication of its
a) Distance from the earth
b) Size
c) Temperature
d) Mass
4 thoughts on “MCQ ON THERMAL PROPERTIES OF MATTER ”